Hypoxia-induced miR-191-C/EBPβ signaling regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 30894209
- PMCID: PMC6425666
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-019-1861-7
Hypoxia-induced miR-191-C/EBPβ signaling regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Hypoxia plays an important role in the proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLS), leading to pathology of RA. This study was conducted to evaluate hypoxia-induced microRNAs (hypoxamiR) in RA-FLS and its role in the function of RA-FLS.
Methods: RA-FLS were cultured under normoxia (21% O2) or hypoxia (3% O2) condition, followed by a microRNA (miRNA) array analysis. The upregulation of miR-191 by hypoxia was confirmed in RA-FLS and FLS from osteoarthritis (OA) patients by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Transfection of miR-191 mimic and inhibitor was used to investigate the function of miR-191 in RA-FLS. The functional targets of miR-191 were predicted by bioinfomatics and then validated by reporter gene assay.
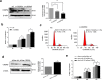
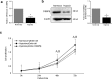
Results: A subset of miRNAs was identified to be induced by hypoxia including miR-191. The upregulation of miR-191 was found to be specific in hypoxic RA-FLS, compared to hypoxic OA-FLS. We observed that miR-191 in RA-FLS increased cellular proliferation via promoting G1/S transition of the cell cycle and suppressed cell apoptosis induced by cell starvation. Bioinformatical analysis and experimental assays identified CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β (C/EBPβ) as a target gene of miR-191 in RA-FLS. Enforced expression of C/EBPβ rescued the cellular phenotypes induced by miR-191. In addition, an inverse correlation between the C/EBPβ level and hypoxia stimulation was found in RA-FLS, and overexpression of C/EBPβ could partly rescue the hypoxia-induced cell proliferation.
Conclusion: We demonstrated the miR-191-C/EBPβ signaling pathway mediating the hypoxia-induced cell proliferation in RA.
Keywords: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β; Fibroblast-like synoviocytes; Hypoxia; Rheumatoid arthritis; miR-191.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-26a-5p enhances cells proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis resistance of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by regulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway.Biosci Rep. 2019 Jul 25;39(7):BSR20182192. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182192. Print 2019 Jul 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31221815 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-199a-3p inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via suppressing retinoblastoma 1.Biosci Rep. 2018 Nov 13;38(6):BSR20180982. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180982. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30352835 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_AFF2 facilitates proliferation and inflammatory response of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via the miR-375/TAB2 axis.Exp Mol Pathol. 2021 Apr;119:104617. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2021.104617. Epub 2021 Jan 31. Exp Mol Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33535081
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase gene BIRC3 modulates TNF-induced cell death pathways and promotes aberrant proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 5;15:1433898. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1433898. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39301019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of glucose metabolism in aggressive phenotype of fibroblast-like synoviocytes: Latest evidence and therapeutic approaches in rheumatoid arthritis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Dec;89(Pt A):107064. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107064. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33039953 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered MicroRNA Maturation in Ischemic Hearts: Implication of Hypoxia on XPO5 and DICER1 Dysregulation and RedoximiR State.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 24;12(7):1337. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071337. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37507877 Free PMC article.
-
The ROS/GRK2/HIF-1α/NLRP3 Pathway Mediates Pyroptosis of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and the Regulation of Monomer Derivatives of Paeoniflorin.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jan 29;2022:4566851. doi: 10.1155/2022/4566851. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35132350 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal MicroRNA-320a Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells Regulates Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte Activation by Suppressing CXCL9 Expression.Front Physiol. 2020 May 26;11:441. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00441. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32528301 Free PMC article.
-
The Transcription Factor C/EBPβ Promotes HFL-1 Cell Migration, Proliferation, and Inflammation by Activating lncRNA HAS2-AS1 in Hypoxia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 12;9:651913. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.651913. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33777961 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Inhibits Osteogenesis and Promotes Adipogenesis of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes via Upregulation of Leptin in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Immunol Res. 2022 Dec 7;2022:1431399. doi: 10.1155/2022/1431399. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36530571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gibofsky A. Overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Manag Care. 2012;18:S295–S302. - PubMed
-
- Sivakumar B, Akhavani MA, Winlove CP, Taylor PC, Paleolog EM, Kang N. Synovial hypoxia as a cause of tendon rupture in rheumatoid arthritis. J HandSurg. 2008;33:49–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

