Dynamic Immune Phenotypes of B and T Helper Cells Mark Distinct Stages of T1D Progression
- PMID: 30894366
- PMCID: PMC6610015
- DOI: 10.2337/db18-1081
Dynamic Immune Phenotypes of B and T Helper Cells Mark Distinct Stages of T1D Progression
Abstract
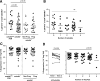
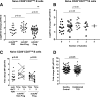
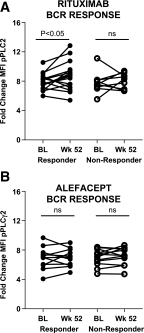
Multiple studies of B- and T-cell compartments and their response to stimuli demonstrate alterations in established type 1 diabetes (T1D). Yet it is not known whether these alterations reflect immune mechanisms that initiate islet autoimmunity, promote disease progression, or are secondary to disease. To address these questions, we used samples from the TrialNet Pathway to Prevention study to investigate T-cell responses to interleukin (IL)-2 and regulatory T cell-mediated suppression, the composition of the B-cell compartment, and B-cell responses to B-cell receptor and IL-21 receptor engagement. These studies revealed stage-dependent T- and B-cell functional and immune phenotypes; namely, early features that differentiate autoantibody-positive at-risk first-degree relatives (FDRs) from autoantibody-negative FDRs and persisted through clinical diagnosis; late features that arose at or near T1D diagnosis; and dynamic features that were enhanced early and blunted at later disease stages, indicating evolving responses along the continuum of T1D. We further explored how these specific phenotypes are influenced by therapeutic interventions. Our integrated studies provide unique insights into stable and dynamic stage-specific immune states and define novel immune phenotypes of potential clinical relevance.
© 2019 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI101990/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK106993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106994/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107014/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP3 DK104466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085504/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085465/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC4 DK090796/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103180/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103282/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103266/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI109565/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107013/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

