Tks5 and Dynamin-2 enhance actin bundle rigidity in invadosomes to promote myoblast fusion
- PMID: 30894403
- PMCID: PMC6504888
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201809161
Tks5 and Dynamin-2 enhance actin bundle rigidity in invadosomes to promote myoblast fusion
Abstract
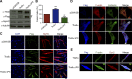
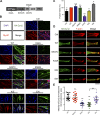
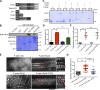
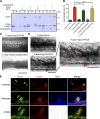
Skeletal muscle development requires the cell-cell fusion of differentiated myoblasts to form muscle fibers. The actin cytoskeleton is known to be the main driving force for myoblast fusion; however, how actin is organized to direct intercellular fusion remains unclear. Here we show that an actin- and dynamin-2-enriched protrusive structure, the invadosome, is required for the fusion process of myogenesis. Upon differentiation, myoblasts acquire the ability to form invadosomes through isoform switching of a critical invadosome scaffold protein, Tks5. Tks5 directly interacts with and recruits dynamin-2 to the invadosome and regulates its assembly around actin filaments to strengthen the stiffness of dynamin-actin bundles and invadosomes. These findings provide a mechanistic framework for the acquisition of myogenic fusion machinery during myogenesis and reveal a novel structural function for Tks5 and dynamin-2 in organizing actin filaments in the invadosome to drive membrane fusion.
© 2019 Chuang et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cdc42 and Tks5: a minimal and universal molecular signature for functional invadosomes.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(3):280-92. doi: 10.4161/cam.28833. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 24840388 Free PMC article.
-
The Innovative Role of Nuclear Receptor Interaction Protein in Orchestrating Invadosome Formation for Myoblast Fusion.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024 Dec;15(6):2559-2573. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13598. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024. PMID: 39323088 Free PMC article.
-
Dependence of myoblast fusion on a cortical actin wall and nonmuscle myosin IIA.Dev Biol. 2009 Jan 15;325(2):374-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.10.035. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19027000 Free PMC article.
-
Myoblast fusion: lessons from flies and mice.Development. 2012 Feb;139(4):641-56. doi: 10.1242/dev.068353. Development. 2012. PMID: 22274696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small GTPases all over invadosomes.Small GTPases. 2021 Sep-Nov;12(5-6):429-439. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2021.1877081. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 33487105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PKCα Induced the Generation of Extracellular Vesicles in Activated Platelets to Promote Breast Cancer Metastasis.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jul 15;20(10):3956-3971. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.89822. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39113702 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Endothelial Transcytosis.Compr Physiol. 2020 Mar 12;10(2):491-508. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c190012. Compr Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32163197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneity and Actin Cytoskeleton in Osteoclast and Macrophage Multinucleation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 10;21(18):6629. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186629. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32927783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
F-actin Bundle Sedimentation Assay.Bio Protoc. 2019 Nov 5;9(21):e3419. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3419. eCollection 2019 Nov 5. Bio Protoc. 2019. PMID: 33654917 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila melanogaster: A Model System to Study Distinct Genetic Programs in Myoblast Fusion.Cells. 2022 Jan 19;11(3):321. doi: 10.3390/cells11030321. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159130 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

