Lysosome inhibition sensitizes pancreatic cancer to replication stress by aspartate depletion
- PMID: 30894490
- PMCID: PMC6452719
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1812410116
Lysosome inhibition sensitizes pancreatic cancer to replication stress by aspartate depletion
Abstract
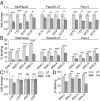
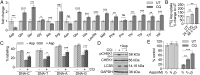
Functional lysosomes mediate autophagy and macropinocytosis for nutrient acquisition. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tumors exhibit high basal lysosomal activity, and inhibition of lysosome function suppresses PDAC cell proliferation and tumor growth. However, the codependencies induced by lysosomal inhibition in PDAC have not been systematically explored. We performed a comprehensive pharmacological inhibition screen of the protein kinome and found that replication stress response (RSR) inhibitors were synthetically lethal with chloroquine (CQ) in PDAC cells. CQ treatment reduced de novo nucleotide biosynthesis and induced replication stress. We found that CQ treatment caused mitochondrial dysfunction and depletion of aspartate, an essential precursor for de novo nucleotide synthesis, as an underlying mechanism. Supplementation with aspartate partially rescued the phenotypes induced by CQ. The synergy of CQ and the RSR inhibitor VE-822 was comprehensively validated in both 2D and 3D cultures of PDAC cell lines, a heterotypic spheroid culture with cancer-associated fibroblasts, and in vivo xenograft and syngeneic PDAC mouse models. These results indicate a codependency on functional lysosomes and RSR in PDAC and support the translational potential of the combination of CQ and RSR inhibitors.
Keywords: autophagy; lysosome; nucleotide metabolism; pancreatic cancer; replication stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
UBL4A inhibits autophagy-mediated proliferation and metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via targeting LAMP1.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jul 9;38(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1278-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31288830 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent Inhibition of IGF1R and ERK Increases Pancreatic Cancer Sensitivity to Autophagy Inhibitors.Cancer Res. 2022 Feb 15;82(4):586-598. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-1443. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 34921013 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibition is synthetically lethal with arginine deprivation in pancreatic cancers with low argininosuccinate synthetase 1 expression.Theranostics. 2020 Jan 1;10(2):829-840. doi: 10.7150/thno.40195. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 31903153 Free PMC article.
-
Co-delivery of autophagy inhibitor and gemcitabine using a pH-activatable core-shell nanobomb inhibits pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis.Theranostics. 2021 Aug 4;11(18):8692-8705. doi: 10.7150/thno.60437. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34522207 Free PMC article.
-
An Eye in the Replication Stress Response: Lessons From Tissue-Specific Studies in vivo.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 4;9:731308. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.731308. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34805142 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GSK3B induces autophagy by phosphorylating ULK1.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Mar;53(3):369-383. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00570-6. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33654220 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging mechanisms and promising approaches in pancreatic cancer metabolism.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Aug 1;15(8):553. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06930-0. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39090116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoinositide specific phospholipase Cγ1 inhibition-driven autophagy caused cell death in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells in vivo and in vitro.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Feb 21;16(8):1427-1440. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.42962. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32210730 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria-targeted magnolol inhibits OXPHOS, proliferation, and tumor growth via modulation of energetics and autophagy in melanoma cells.Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2020;25:100210. doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2020.100210. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32987287 Free PMC article.
-
An Asp to Strike Out Cancer? Therapeutic Possibilities Arising from Aspartate's Emerging Roles in Cell Proliferation and Survival.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 10;11(11):1666. doi: 10.3390/biom11111666. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827664 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed

