OR14I1 is a receptor for the human cytomegalovirus pentameric complex and defines viral epithelial cell tropism
- PMID: 30894498
- PMCID: PMC6452726
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1814850116
OR14I1 is a receptor for the human cytomegalovirus pentameric complex and defines viral epithelial cell tropism
Abstract
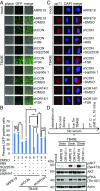
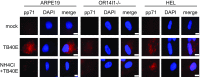
A human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) pentameric glycoprotein complex (PC), gH-gL-UL128-UL130-UL131A, is necessary for viral infection of clinically relevant cell types, including epithelial cells, which are important for interhost transmission and disease. We performed genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screens of different cell types in parallel to identify host genes specifically required for HCMV infection of epithelial cells. This effort identified a multipass membrane protein, OR14I1, as a receptor for HCMV infection. This olfactory receptor family member is required for HCMV attachment, entry, and infection of epithelial cells and is dependent on the presence of viral PC. OR14I1 is required for AKT activation and mediates endocytosis entry of HCMV. We further found that HCMV infection of epithelial cells is blocked by a synthetic OR14I1 peptide and inhibitors of adenylate cyclase and protein kinase A (PKA) signaling. Identification of OR14I1 as a PC-dependent HCMV host receptor associated with epithelial tropism and the role of the adenylate cyclase/PKA/AKT-mediated signaling pathway in HCMV infection reveal previously unappreciated targets for the development of vaccines and antiviral therapies.
Keywords: CRISPR screen; OR14I1; human cytomegalovirus; pentameric glycoprotein complex; virus receptor.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: X.E., A.L.B., and T.F.K. are listed as coinventors in a patent application based in part on data from this study.
Figures
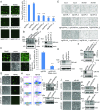

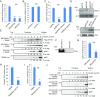
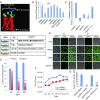
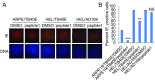
References
-
- Britt W. Manifestations of human cytomegalovirus infection: Proposed mechanisms of acute and chronic disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:417–470. - PubMed
-
- Dollard SC, Grosse SD, Ross DS. New estimates of the prevalence of neurological and sensory sequelae and mortality associated with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Rev Med Virol. 2007;17:355–363. - PubMed
-
- Kenneson A, Cannon MJ. Review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Rev Med Virol. 2007;17:253–276. - PubMed
-
- Sinzger C, Digel M, Jahn G. Cytomegalovirus cell tropism. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:63–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

