CHK1 dosage in germinal center B cells controls humoral immunity
- PMID: 30894677
- PMCID: PMC7224292
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-019-0318-5
CHK1 dosage in germinal center B cells controls humoral immunity
Abstract
Germinal center (GC) B cells are among the fastest replicating cells in our body, dividing every 4-8 h. DNA replication errors are intrinsically toxic to cells. How GC B cells exert control over the DNA damage response while introducing mutations in their antibody genes is poorly understood. Here, we show that the DNA damage response regulator Checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK1) is essential for GC B cell survival. Remarkably, effective antibody-mediated immunity relies on optimal CHK1 dosage. Chemical CHK1 inhibition or loss of one Chk1 allele impairs the survival of class-switched cells and curbs the amplitude of antibody production. Mechanistically, active B cell receptor signaling wires the outcome of CHK1-inhibition towards BIM-dependent apoptosis, whereas T cell help favors temporary cell cycle arrest. Our results predict that therapeutic CHK1 inhibition in cancer patients may prove potent in killing B cell lymphoma and leukemia cells addicted to B cell receptor signaling, but will most likely dampen humoral immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
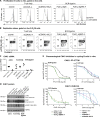

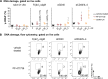
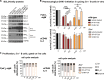
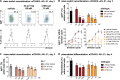
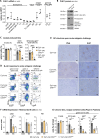
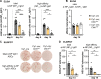
References
-
- Shlomchik MJ, Weisel F. Germinal center selection and the development of memory B and plasma cells. Immunol Rev. 2012;247:52–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- I 1298/Austrian Science Fund (Fonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung)
- P 26856/Austrian Science Fund (Fonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung)
- Doctoral College "Molecular Cell Biology and Oncology" (W1101)/Austrian Science Fund (Fonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung)
- DOC PhD Fellowship/Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften (Austrian Academy of Sciences)
- P 28694/FWF_/Austrian Science Fund FWF/Austria
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

