Epigenetics and epigenomics in diabetic kidney disease and metabolic memory
- PMID: 30894700
- PMCID: PMC6889804
- DOI: 10.1038/s41581-019-0135-6
Epigenetics and epigenomics in diabetic kidney disease and metabolic memory
Abstract
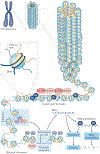
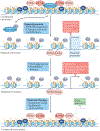
The development and progression of diabetic kidney disease (DKD), a highly prevalent complication of diabetes mellitus, are influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. DKD is an important contributor to the morbidity of patients with diabetes mellitus, indicating a clear need for an improved understanding of disease aetiology to inform the development of more efficacious treatments. DKD is characterized by an accumulation of extracellular matrix, hypertrophy and fibrosis in kidney glomerular and tubular cells. Increasing evidence shows that genes associated with these features of DKD are regulated not only by classical signalling pathways but also by epigenetic mechanisms involving chromatin histone modifications, DNA methylation and non-coding RNAs. These mechanisms can respond to changes in the environment and, importantly, might mediate the persistent long-term expression of DKD-related genes and phenotypes induced by prior glycaemic exposure despite subsequent glycaemic control, a phenomenon called metabolic memory. Detection of epigenetic events during the early stages of DKD could be valuable for timely diagnosis and prompt treatment to prevent progression to end-stage renal disease. Identification of epigenetic signatures of DKD via epigenome-wide association studies might also inform precision medicine approaches. Here, we highlight the emerging role of epigenetics and epigenomics in DKD and the translational potential of candidate epigenetic factors and non-coding RNAs as biomarkers and drug targets for DKD.
Figures


References
-
- Zimmet PZ, Magliano DJ, Herman WH & Shaw JE Diabetes: a 21st century challenge. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2, 56–64, (2014). - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM Long-term complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 328, 1676–1685, (1993). - PubMed
-
- Forbes JM & Cooper ME Mechanisms of Diabetic Complications. Physiol Rev 93, 137–188, (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

