A retrospective review of multiple findings in diagnostic exome sequencing: half are distinct and half are overlapping diagnoses
- PMID: 30894705
- PMCID: PMC6774997
- DOI: 10.1038/s41436-019-0477-2
A retrospective review of multiple findings in diagnostic exome sequencing: half are distinct and half are overlapping diagnoses
Abstract
Purpose: We evaluated clinical and genetic features enriched in patients with multiple Mendelian conditions to determine which patients are more likely to have multiple potentially relevant genetic findings (MPRF).
Methods: Results of the first 7698 patients who underwent exome sequencing at Ambry Genetics were reviewed. Clinical and genetic features were examined and degree of phenotypic overlap between the genetic diagnoses was evaluated.
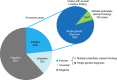
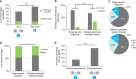
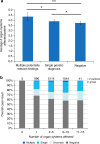
Results: Among patients referred for exome sequencing, 2% had MPRF. MPRF were more common in patients from consanguineous families and patients with greater clinical complexity. The difference in average number of organ systems affected is small: 4.3 (multiple findings) vs. 3.9 (single finding) and may not be distinguished in clinic.
Conclusion: Patients with multiple genetic diagnoses had a slightly higher number of organ systems affected than patients with single genetic diagnoses, largely because the comorbid conditions affected overlapping organ systems. Exome testing may be beneficial for all cases with multiple organ systems affected. The identification of multiple relevant genetic findings in 2% of exome patients highlights the utility of a comprehensive molecular workup and updated interpretation of existing genomic data; a single definitive molecular diagnosis from analysis of a limited number of genes may not be the end of a diagnostic odyssey.
Keywords: comorbidity; diagnostic exome sequencing; distinct vs. overlapping phenotypes; multilocus genomic variation; multiple genetic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
E.D.S., K.R., K.B., S.A.S., J.M.H., D.N.S., B.W., M.R., J.H., W.A., K.D.F.H. and S.T. are full-time, salaried employees of Ambry Genetics. Diagnostic exome sequencing is one of the publicly available tests offered by Ambry Genetics. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

