Surgical considerations and management of bilateral labially impacted canines
- PMID: 30894972
- PMCID: PMC6395172
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2013.02.027
Surgical considerations and management of bilateral labially impacted canines
Abstract
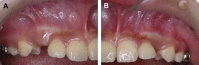
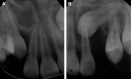
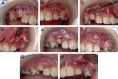
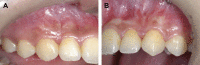
Canines are among the most commonly impacted teeth. When a canine is positioned labially, the untoward soft-tissue responses following surgical exposure may cause unfavorable esthetic outcomes. Therefore, decision making as to the choice of a proper surgical technique to uncover labially impacted teeth is critical. This case presentation describes two different surgical approaches for two maxillary impacted canines in a 12-year-old girl. A sequential approach included a first stage of surgical exposure using apically positioned flaps and orthodontic extrusion of both impacted teeth. A successive laterally positioned flap was used for the left maxillary canine to achieve a harmonious soft-tissue contour. In this case, close monitoring and cooperation during the various treatment phases led to proper canine positioning and a successful esthetic result, with good periodontal health and functional occlusion.
Keywords: canine impaction; mucogingival surgery; surgical exposure.
Figures

References
-
- Dachi S.F., Howell F.V. A survey of 3874 routine full mouth radiographs: II. A study of impacted teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1961;14:1165–1169. - PubMed
-
- Thilander B., Myberg N. The prevalence of malocclusion in Swedish school children. Scand J Dent Res. 1971;81:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Johnston W.D. Treatment of palatally impacted canine teeth. Am J Orthod. 1969;56:589–596. - PubMed
-
- Kokich V.G. Surgical and orthodontic management of impacted maxillary canines. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2004;126:278–283. - PubMed
-
- Kokich V.G., Mathews D.P. Surgical and orthodontic management of impacted teeth. Dent Clin North Am. 1993;37:181–204. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

