Enamel lesions: Meta-analysis on effect of prophylactic/therapeutic agents in erosive tissue loss
- PMID: 30894976
- PMCID: PMC6395268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2016.03.008
Enamel lesions: Meta-analysis on effect of prophylactic/therapeutic agents in erosive tissue loss
Abstract
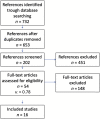
This study aims to perform a meta-analysis on the effect of prophylactic/therapeutic agents in enamel tissue loss due to erosion. A paper search was done on Medline, PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library, and 732 papers were identified. The inclusion criteria were very restrictive in order to be able to compare different protocols and methodologies used on those studies. Sixteen papers were eligible, grouped according to the measurement method of enamel tissue loss, and a meta-analysis was done for each type of fluoride- and casein-based agent applied. Standardized mean differences were pooled across studies. There was a significant difference between all the treatment groups and their respective control groups. The highest standardized mean difference on enamel tissue loss (mean; 95% confidence interval) was obtained by stannous fluoride (4.789 μm; 1.968-7.610; P < 0.001), followed by amine fluoride (2.485 μm; 0.746-4.225; P < 0.010), and titanium tetrafluoride (1.787 μm; 1.106-2.469; P < 0.001); the lowest difference was obtained by casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (0.869 μm; 0.007-1.731; P < 0.050) and sodium fluoride (0.820 μm; 0.417-1.223; P < 0.001). Stannous fluoride as a fluoride-based prophylactic/therapeutic agent allowed the lowest enamel tissue loss in erosive conditions. Standardization among future study protocols will allow better comparison regarding the prophylactic/therapeutic agent with the best clinical efficacy.
Keywords: caseins; demineralization; enamel; erosion; fluorides.
Figures



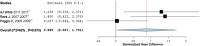



Similar articles
-
Remineralizing Effect of Casein Phosphopeptide-Amorphous Calcium Phosphate and Sodium Fluoride on Artificial Tooth Enamel Erosion: An In Vitro Study.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2019 Nov 1;20(11):1254-1259. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2019. PMID: 31892675
-
The Effect of Casein Phosphopeptide-Amorf Calcium Phosphate and Acidulated Phosphate Fluoride Gel on Dental Erosion in Primary Teeth: An in Vitro Study.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2017;41(4):275-279. doi: 10.17796/1053-4628-41.4.275. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2017. PMID: 28650787 Clinical Trial.
-
Preventive effects of carbon dioxide laser and casein phosphopeptide amorphous calcium phosphate fluoride varnish on enamel demineralization: A comparative, in vitro study.J Investig Clin Dent. 2019 May;10(2):e12400. doi: 10.1111/jicd.12400. Epub 2019 Jan 28. J Investig Clin Dent. 2019. PMID: 30693660
-
Bioavailable gluconate chelated stannous fluoride toothpaste meta-analyses: Effects on dentine hypersensitivity and enamel erosion.J Dent. 2021 Feb;105:103566. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2020.103566. Epub 2020 Dec 28. J Dent. 2021. PMID: 33383100 Review.
-
Protective effect of fluorides on erosion and erosion/abrasion in enamel: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized in situ trials.Arch Oral Biol. 2020 Dec;120:104945. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2020.104945. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Arch Oral Biol. 2020. PMID: 33113459
Cited by
-
A Comparative Study of the Effect of Tooth Mousse Plus Remin Pro and Fluor Protector Gel on Enamel Erosion: An In Vitro Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023 Aug;16(Suppl 1):S57-S62. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2602. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023. PMID: 37663219 Free PMC article.
-
Preventing dentin erosion with silver diamine fluoride and salivary pellicle: an in vitro study.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Oct 8;28(11):577. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05988-6. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 39377799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Imfeld T. Dental erosion. Definition, classification and links. Eur J Oral Sci. 1996;104:151–155. - PubMed
-
- Addy M., Shellis R.P. Interaction between attrition, abrasion and erosion in tooth wear. In: Lussi A., editor. Dental Erosion: From Diagnosis to Therapy. Monogr Oral Sci. Karger; Basel: 2006. 20:17. se. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Z.J., Wang X.M., Cui F.Z., Ge J., Yan J.X. The enamel softening and loss during early erosion studied by AFM, SEM and nanoindentation. Biomed Mater. 2009;4:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Zero D.T., Lussi A. Behavioural factors. Monogr Oral Sci. 2006;20:100–105. - PubMed
-
- Zero D.T., Hara A.T., Kelly S.A. Evaluation of a desensitising test dentifrice using an in situ erosion remineralisation model. J Clin Dent. 2006;17:112–116. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

