Increased cyclooxygenase 2 expression in association with oral lichen planus severity
- PMID: 30894979
- PMCID: PMC6395257
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2015.12.002
Increased cyclooxygenase 2 expression in association with oral lichen planus severity
Abstract
Background/purpose: Although some studies have shown induction of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) in oral lichen planus (OLP), an association between COX-2 upregulation and OLP clinical severity has not been investigated. Therefore, we aimed to compare COX-2 expression in OLP with that in normal oral tissues, and to determine correlations between COX-2 expression and both clinical criteria and visual analog scale (VAS) scores.
Materials and methods: COX-2 expression was studied in 25 OLP and 13 normal oral tissues by immunohistochemistry. Both clinical criteria and VAS scores were used to evaluate the clinical severity of OLP. The differences in COX-2 expression between OLP and normal tissues, and the correlations between COX-2 expression and clinical severity were determined by the nonparametric statistical tests.
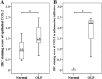
Results: COX-2 expression was significantly increased in OLP epithelium when compared with normal epithelium (P < 0.001), and intense COX-2 staining in inflammatory infiltrates was observed in the OLP lamina propria. COX-2 expression in OLP epithelium and inflammatory infiltrates was significantly correlated with the clinical criteria score (r = 0.428, P = 0.007, and r = 0.681, P < 0.001, respectively), whereas a significant correlation with the VAS score was observed only in OLP inflammatory infiltrates (r = 0.605, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Enhanced COX-2 expression in both OLP epithelium and inflammatory infiltrates correlates well with the clinical severity. An association between VAS score and COX-2 expression in OLP inflammatory infiltrates suggests an important role of additional COX-2 expression from inflammation in causing pain in OLP patients.
Keywords: cyclooxygenase 2; immunohistochemistry; oral lichen planus; visual analog pain scale.
Figures



References
-
- Carrozzo M., Gandolfo S. The management of oral lichen planus. Oral Dis. 1999;5:196–205. - PubMed
-
- Al-Hashimi I., Schifter M., Lockhart P.B. Oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid lesions: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;103 S25.e1–12. - PubMed
-
- Baccaglini L., Thongprasom K., Carrozzo M., Bigby M. Urban legends series: lichen planus. Oral Dis. 2013;19:128–143. - PubMed
-
- Thongprasom K., Youngnak-Piboonratanakit P., Pongsiriwet S., Laothumthut T., Kanjanabud P., Rutchakitprakarn L. A multicenter study of oral lichen planus in Thai patients. J Investig Clin Dent. 2010;1:29–36. - PubMed
-
- Sugerman P.B., Savage N.W., Walsh L.J. The pathogenesis of oral lichen planus. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002;13:350–365. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

