A trial to evaluate the effect of the sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (DAPA-HF)
- PMID: 30895697
- PMCID: PMC6607736
- DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.1432
A trial to evaluate the effect of the sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (DAPA-HF)
Abstract
Background: Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have been shown to reduce the risk of incident heart failure hospitalization in individuals with type 2 diabetes who have, or are at high risk of, cardiovascular disease. Most patients in these trials did not have heart failure at baseline and the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on outcomes in individuals with established heart failure (with or without diabetes) is unknown.
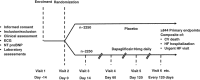
Design and methods: The Dapagliflozin And Prevention of Adverse-outcomes in Heart Failure trial (DAPA-HF) is an international, multicentre, parallel group, randomized, double-blind, study in patients with chronic heart failure, evaluating the effect of dapagliflozin 10 mg, compared with placebo, given once daily, in addition to standard care, on the primary composite outcome of a worsening heart failure event (hospitalization or equivalent event, i.e. an urgent heart failure visit) or cardiovascular death. Patients with and without diabetes are eligible and must have a left ventricular ejection fraction ≤ 40%, a moderately elevated N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide level, and an estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥ 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 . The trial is event-driven, with a target of 844 primary outcomes. Secondary outcomes include the composite of total heart failure hospitalizations (including repeat episodes), and cardiovascular death and patient-reported outcomes. A total of 4744 patients have been randomized.
Conclusions: DAPA-HF will determine the efficacy and safety of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin, added to conventional therapy, in a broad spectrum of patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction.
Keywords: Clinical trial; Heart failure; Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2019 The Authors. European Journal of Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
References
-
- McMurray JJ, Gerstein HC, Holman RR, Pfeffer MA. Heart failure: a cardiovascular outcome in diabetes that can no longer be ignored. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014;2:843–851. - PubMed
-
- Seferović PM, Petrie MC, Filippatos GS, Anker SD, Rosano G, Bauersachs J, Paulus WJ, Komajda M, Cosentino F, de Boer RA, Farmakis D, Doehner W, Lambrinou E, Lopatin Y, Piepoli MF, Theodorakis MJ, Wiggers H, Lekakis J, Mebazaa A, Mamas MA, Tschöpe C, Hoes AW, Seferović JP, Logue J, McDonagh T, Riley JP, Milinković I, Polovina M, van Veldhuisen DJ, Lainscak M, Maggioni AP, Ruschitzka F, McMurray JJ. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure: a position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail 2018;20:853–872. - PubMed
-
- Lago RM, Singh PP, Nesto RW. Congestive heart failure and cardiovascular death in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes given thiazolidinediones: a meta‐analysis of randomised clinical trials. Lancet 2007;370:1129–1136. - PubMed
-
- Scirica BM, Braunwald E, Raz I, Cavender MA, Morrow DA, Jarolim P, Udell JA, Mosenzon O, Im K, Umez‐Eronini AA, Pollack PS, Hirshberg B, Frederich R, Lewis BS, McGuire DK, Davidson J, Steg PG, Bhatt DL; SAVOR‐TIMI 53 Steering Committee and Investigators . Heart failure, saxagliptin, and diabetes mellitus: observations from the SAVOR‐TIMI 53 randomized trial. Circulation 2015;132:e198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous