Silencing the lncRNA Maclpil in pro-inflammatory macrophages attenuates acute experimental ischemic stroke via LCP1 in mice
- PMID: 30895879
- PMCID: PMC7168792
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X19836118
Silencing the lncRNA Maclpil in pro-inflammatory macrophages attenuates acute experimental ischemic stroke via LCP1 in mice
Abstract
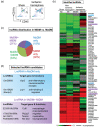
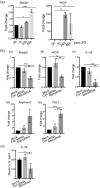
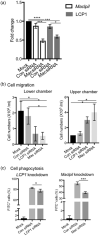
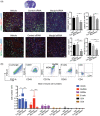
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNA) expression profiles change in the ischemic brain after stroke, but their roles in specific cell types after stroke have not been studied. We tested the hypothesis that lncRNA modulates brain injury by altering macrophage functions. Using RNA deep sequencing, we identified 73 lncRNAs that were differentially expressed in monocyte-derived macrophages (MoDMs) and microglia-derived macrophages (MiDMs) isolated in the ischemic brain three days after stroke. Among these, the lncRNA, GM15628, is highly expressed in pro-inflammatory MoDMs but not in MiDMs, and are functionally related to its neighbor gene, lymphocyte cytosolic protein 1 (LCP1), which plays a role in maintaining cell shape and cell migration. We termed this lncRNA as
Keywords: Inflammatory; Ischemic stroke; lncRNA; macrophages; neuroinflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics – 2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015; 131: e29–322. - PubMed
-
- Menon BK, Saver JL, Goyal M, et al. Trends in endovascular therapy and clinical outcomes within the nationwide Get With The Guidelines-Stroke registry. Stroke 2015; 46: 989–995. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

