Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody is highly associated with rheumatoid factor and radiological defects in rheumatoid arthritis patients
- PMID: 30896663
- PMCID: PMC6709297
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014945
Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody is highly associated with rheumatoid factor and radiological defects in rheumatoid arthritis patients
Abstract
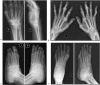
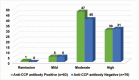
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic debilitating inflammatory disease affecting mainly the joint, surrounding tissue and other extra-articular structures in the body. RA can lead to destruction of bone and cartilage which may cause severe disability and it is characterized by the presence of serum rheumatoid factor (RF). The anti-cyclic citrullinate peptide (anti-CCP) antibody is another serum biomarker used in RA diagnosis with higher sensitivity and specificity.In this cross-sectional study with retrospective record review, 159 established RA patients from Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia (HUSM) were recruited. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) for serum RF and anti-CCP were performed. Our goal was to evaluate the significance of anti-CCP antibody in predicting the disease activity and progression in terms of radiological and extra-articular manifestations upon diagnosis.Of the 159 RA patients included in this study, mean age was 48.3 years old and majority (n = 134; 84.3%) were female. A total of 83 (52.2%) and 99 (62.3%) patients had anti-CCP antibody and RF, respectively. Mean Disease Activity Score-28 for Rheumatoid Arthritis with erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (DAS28-ESR) score for all patients was 4.74 (medium and high disease activity). Fifty-eight (36.5%) patients had radiological defects and 49 (30.8%) patients had extra-articular involvement manifested by rheumatoid nodule, pulmonary involvement, and anemia.In terms of anti-CCP antibody association with clinical and laboratory parameters, a significant co-occurrence of RF and anti-CCP antibody (P = .002) was observed. Anti-CCP antibody was significantly associated with radiological defects in which majority of patients with such defects (n = 40/58; 68.9%) were positive for anti-CCP antibody (P = .001). However, there was no significant difference between mean and classes of disease activity score and extra-articular manifestations between different anti-CCP antibody groups. In addition, extra-articular manifestations were not associated with high disease activity upon RA diagnosisThere was a significant association between anti-CCP antibody positivity and positive RF. Radiological defects were the sole clinical parameter significantly associated with anti-CCP antibody positivity, indicating that patients positive for anti-CCP antibody should be routinely monitored for radiological defects and their onset.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide but not rheumatoid factor is associated with ultrasound-detected bone erosion among rheumatoid arthritis patients with at least moderate disease activity.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Oct;23(10):1337-1343. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13933. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 33460311
-
Autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: association with severity of disease in established RA.Clin Rheumatol. 2007 Feb;26(2):201-4. doi: 10.1007/s10067-006-0275-5. Epub 2006 Mar 30. Clin Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 16572283
-
Rheumatoid factor and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies with hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection: Review.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017 Sep;26(6):987-990. doi: 10.17219/acem/63095. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 29068601
-
Meta-analysis: compared with anti-CCP and rheumatoid factor, could anti-MCV be the next biomarker in the rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria?Clin Chem Lab Med. 2019 Oct 25;57(11):1668-1679. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2019-0167. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 31141478 Review.
-
Autoantibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis - Laboratory and Clinical Perspectives.Front Immunol. 2021 May 14;12:685312. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.685312. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054878 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Risk Factors Associated with Adverse Events Leading to Methotrexate Withdrawal in Elderly Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 24;13(7):1863. doi: 10.3390/jcm13071863. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38610627 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction model for bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis based on musculoskeletal ultrasound and clinical risk factors.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jan;44(1):143-152. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07219-5. Epub 2024 Nov 9. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39520586
-
EBNA1 IgM-Based Discrimination Between Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients and Healthy Controls.Antibodies (Basel). 2019 Jun 1;8(2):35. doi: 10.3390/antib8020035. Antibodies (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31544841 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the risk of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease related to anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) antibody.BMJ Open. 2021 Mar 31;11(3):e040465. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-040465. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 33789847 Free PMC article.
-
A sequencing study of CTLA4 in Pakistani rheumatoid arthritis cases.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 18;15(9):e0239426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239426. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32946523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alamanos Y, Drosos AA. Epidemiology of adult rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 2005;4:130–6. - PubMed
-
- Niewold TB, Harrison MJ, Paget SA. Anti-CCP antibody testing as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. QJM 2007;100:193–201. - PubMed
-
- Szekanecz Z, Soos L, Szabo Z, et al. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: as good as it gets? Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2008;34:26–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

