The Role of Disease Label in Patient Perceptions and Treatment Decisions in the Setting of Low-Risk Malignant Neoplasms
- PMID: 30896738
- PMCID: PMC6567830
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.0054
The Role of Disease Label in Patient Perceptions and Treatment Decisions in the Setting of Low-Risk Malignant Neoplasms
Abstract
Importance: The cancer disease label may lead to overtreatment of low-risk malignant neoplasms owing to a patient's emotional response or misunderstanding of prognosis. Decision making should be driven by risks and benefits of treatment and prognosis rather than disease label.
Objective: To determine whether disease label plays a role in patient decision making in the setting of low-risk malignant neoplasms and to determine how the magnitude of the disease-label effect compares with preferences for treatment and prognosis.
Design, setting, and participants: A discrete choice experiment conducted using an online survey of 1314 US residents in which participants indicated their preferences between a series of 2 hypothetical vignettes describing the incidental discovery of a small thyroid lesion. Vignettes varied on 3 attributes: disease label (cancer, tumor, or nodule); treatment (active surveillance or hemithyroidectomy); and risk of progression or recurrence (0%, 1%, 2%, or 5%). The independent associations of each attribute with likelihood of vignette selection was estimated with a Bayesian mixed logit model.
Main outcomes and measures: The preference weight of the cancer disease label was compared with preference weights for other attributes.
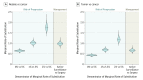
Results: In 1068 predominantly healthy respondents (605 women and 463 men) with a median age of 35 years (range, 18-78 years), the cancer disease label played a considerable role in respondent decision making independent of treatment offered and risk of progression or recurrence. Participants accepted a 4-percentage-point increase in risk of progression or recurrence (from 1% to 5%) to avoid labeling their disease as cancer in favor of nodule (marginal rate of substitution [MRS], 1.0; 95% credible interval [CrI], 0.9-1.1). Preference for the nodule label instead of cancer was similar in magnitude to the preference for active surveillance over surgery (MRS, 1.0; 95% CrI, 0.9-1.1).
Conclusions and relevance: Disease label plays a role in patient preference independent of treatment risks or prognosis. Raising the threshold for biopsy or removing the word cancer from the disease label may mitigate patient preference for aggressive treatment of low-risk lesions. Health care professionals should emphasize treatment risks and benefits and natural disease history when supporting treatment decisions for potentially innocuous epithelial malignant neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Disease Labels and Clear Communication With Patients-A Rose by Any Other Name Would Smell as Sweet.JAMA Oncol. 2019 Jun 1;5(6):784-785. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.0053. JAMA Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30896753 No abstract available.
References
-
- Strickland KC, Eszlinger M, Paschke R, et al. . Molecular testing of nodules with a suspicious or malignant cytologic diagnosis in the setting of non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP). Endocr Pathol. 2018;29(1):68-74. doi:10.1007/s12022-018-9515-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. , eds. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975-2014, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, based on November 2016 SEER data submission posted to the SEER website, April 2017. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2014/. Accessed January 3, 2018.
-
- Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, et al. . 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2016;26(1):1-133. doi:10.1089/thy.2015.0020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

