Targeting bacterial quorum sensing shows promise in improving intestinal barrier function following burn‑site infection
- PMID: 30896813
- PMCID: PMC6472113
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10071
Targeting bacterial quorum sensing shows promise in improving intestinal barrier function following burn‑site infection
Abstract
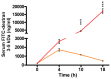
Burn‑site infections, commonly due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, have been associated with deranged intestinal integrity, allowing bacteria and their products to translocate from the gut to the circulatory system. The P. aeruginosa quorum sensing (QS) transcription factor MvfR (PqsR) controls the expression of numerous virulence factors, and the synthesis of several toxic products. However, the role of QS in intestinal integrity alterations, to the best of our knowledge, has not been previously investigated. Using a proven anti‑MvfR, anti‑virulence agent, the in vivo results of the present study revealed that inhibition of MvfR function significantly decreased Fluorescein Isothiocyanate‑Dextran (FITC‑Dextran) flow from the intestine to the systemic circulation, diminished bacterial translocation from the intestine to mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs), and improved tight junction integrity in thermally injured and infected mice. In addition, the MvfR antagonist administration alleviates the intestinal inflammation, as demonstrated by reduced ileal TNF‑α and fecal lipocalin‑2 concentrations. In addition, it is associated with lower levels of circulating endotoxin and decreased P. aeruginosa dissemination from the burn wound to the ileum. Collectively, these results hold great promise that the inhibition of this QS system mitigates gut hyperpermeability by attenuating the derangement of morphological and immune aspects of the intestinal barrier, suggesting that MvfR function is crucial in the deterioration of intestinal integrity following P. aeruginosa burn‑site infection. Therefore, an anti‑virulence approach targeting MvfR, could potentially offer a novel therapeutic approach against multi‑drug resistant P. aeruginosa infections following thermal injuries. Since this approach is targeting virulence pathways that are non‑essential for growth or viability, our strategy is hypothesized to minimize the development of bacterial resistance, and preserve the beneficial enteric microbes, while improving intestinal integrity that is deranged as a result of burn and infection.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tackling recalcitrant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in critical illness via anti-virulence monotherapy.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 30;13(1):5103. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32833-9. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36042245 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing transcription factor MvfR: reversing effects with anti-MvfR and mitochondrial-targeted compounds.mBio. 2024 Jul 17;15(7):e0129224. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01292-24. Epub 2024 Jun 11. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38860823 Free PMC article.
-
Interconnections of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum-Sensing Systems in Intestinal Permeability and Inflammation.mBio. 2023 Apr 25;14(2):e0352422. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03524-22. Epub 2023 Feb 14. mBio. 2023. PMID: 36786582 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-PqsR compounds as next-generation antibacterial agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Jun 15;172:26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.049. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30939351 Review.
-
Chemical probes of quorum sensing: from compound development to biological discovery.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016 Sep;40(5):774-94. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuw009. Epub 2016 Jun 5. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27268906 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tackling recalcitrant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in critical illness via anti-virulence monotherapy.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 30;13(1):5103. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32833-9. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36042245 Free PMC article.
-
Breast and gut microbiome in health and cancer.Genes Dis. 2020 Aug 20;8(5):581-589. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.08.002. eCollection 2021 Sep. Genes Dis. 2020. PMID: 34291130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Making Sense of Quorum Sensing at the Intestinal Mucosal Interface.Cells. 2022 May 24;11(11):1734. doi: 10.3390/cells11111734. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quorum sensing-related activities of beneficial and pathogenic bacteria have important implications for plant and human health.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2024 May 14;100(6):fiae076. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiae076. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2024. PMID: 38744663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the gut to prevent sepsis from a cutaneous burn.JCI Insight. 2020 Oct 2;5(19):e137128. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.137128. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 33004693 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

