Macrophage nuclear receptors: Emerging key players in infectious diseases
- PMID: 30897154
- PMCID: PMC6428245
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007585
Macrophage nuclear receptors: Emerging key players in infectious diseases
Abstract
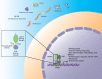
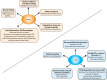
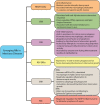
Nuclear receptors (NRs) are ligand-activated transcription factors that are expressed in a variety of cells, including macrophages. For decades, NRs have been therapeutic targets because their activity can be pharmacologically modulated by specific ligands and small molecule inhibitors. NRs regulate a variety of processes, including those intersecting metabolic and immune functions, and have been studied in regard to various autoimmune diseases. However, the complex roles of NRs in host response to infection are only recently being investigated. The NRs peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and liver X receptors (LXRs) have been most studied in the context of infectious diseases; however, recent work has also linked xenobiotic pregnane X receptors (PXRs), vitamin D receptor (VDR), REV-ERBα, the nuclear receptor 4A (NR4A) family, farnesoid X receptors (FXRs), and estrogen-related receptors (ERRs) to macrophage responses to pathogens. Pharmacological inhibition or antagonism of certain NRs can greatly influence overall disease outcome, and NRs that are protective against some diseases can lead to susceptibility to others. Targeting NRs as a novel host-directed treatment approach to infectious diseases appears to be a viable option, considering that these transcription factors play a pivotal role in macrophage lipid metabolism, cholesterol efflux, inflammatory responses, apoptosis, and production of antimicrobial byproducts. In the current review, we discuss recent findings concerning the role of NRs in infectious diseases with an emphasis on PPARγ and LXR, the two most studied. We also highlight newer work on the activity of emerging NRs during infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

