Structural determination of the complement inhibitory domain of Borrelia burgdorferi BBK32 provides insight into classical pathway complement evasion by Lyme disease spirochetes
- PMID: 30897158
- PMCID: PMC6445466
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007659
Structural determination of the complement inhibitory domain of Borrelia burgdorferi BBK32 provides insight into classical pathway complement evasion by Lyme disease spirochetes
Abstract
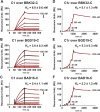
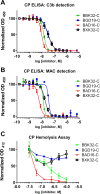
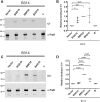
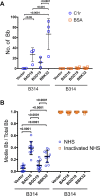
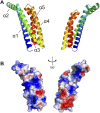
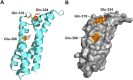
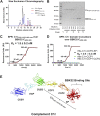
The carboxy-terminal domain of the BBK32 protein from Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, termed BBK32-C, binds and inhibits the initiating serine protease of the human classical complement pathway, C1r. In this study we investigated the function of BBK32 orthologues of the Lyme-associated Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex, designated BAD16 from B. afzelii strain PGau and BGD19 from B. garinii strain IP90. Our data show that B. afzelii BAD16-C exhibits BBK32-C-like activities in all assays tested, including high-affinity binding to purified C1r protease and C1 complex, and potent inhibition of the classical complement pathway. Recombinant B. garinii BGD19-C also bound C1 and C1r with high-affinity yet exhibited significantly reduced in vitro complement inhibitory activities relative to BBK32-C or BAD16-C. Interestingly, natively produced BGD19 weakly recognized C1r relative to BBK32 and BAD16 and, unlike these proteins, BGD19 did not confer significant protection from serum killing. Site-directed mutagenesis was performed to convert BBK32-C to resemble BGD19-C at three residue positions that are identical between BBK32 and BAD16 but different in BGD19. The resulting chimeric protein was designated BXK32-C and this BBK32-C variant mimicked the properties observed for BGD19-C. To query the disparate complement inhibitory activities of BBK32 orthologues, the crystal structure of BBK32-C was solved to 1.7Å limiting resolution. BBK32-C adopts an anti-parallel four-helix bundle fold with a fifth alpha-helix protruding from the helical core. The structure revealed that the three residues targeted in the BXK32-C chimera are surface-exposed, further supporting their potential relevance in C1r binding and inhibition. Additional binding assays showed that BBK32-C only recognized C1r fragments containing the serine protease domain. The structure-function studies reported here improve our understanding of how BBK32 recognizes and inhibits C1r and provide new insight into complement evasion mechanisms of Lyme-associated spirochetes of the B. burgdorferi sensu lato complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

