Efficacy and safety of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors for the treatment of distal ureteral calculi of 5 to 10 mm in size: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 30897293
- PMCID: PMC11900753
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12048
Efficacy and safety of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors for the treatment of distal ureteral calculi of 5 to 10 mm in size: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
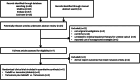
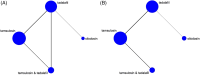
To evaluate the Efficacy and safety of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors as a medical therapy for distal ureteral calculi by means of a systematic review and network meta-analysis (NMA). We searched the Embase, Medline, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials for randomised controlled trials (RCTs) published before May, 2017. Stone passage rate as the primary outcome. We used random effects model for pairwise meta-analyses and Bayesian random effects model for NMA. We evaluated the quality of evidence by the GRADE framework for each network estimate. Five RCTs (861 patients) comparing four different interventions. The results of NMA showed that compared with tamsulosin alone, tamsulosin combined with tadalafil group was associated with significantly higher stone passage rate (odds radio [OR] 2.55, 95% credible intervals [Crl] 1.11 to 5.89). When considering stone expulsion rate, compared with tamsulosin, silodosin was ranked best (OR 3.58, 95% Crl 1.13 to 11.91), followed by tamsulosin combined with tadalafil (OR 2.55, 95% Crl 1.11 to 5.89) and tadalafil alone (OR 1.86, 95% Crl 0.95 to 4.25). No significant difference was found considering safety profiles between any interventions. This meta-analysis indicates that tamsulosin combined with tadalafil is an effective treatment option for ureteral stones with a low occurrence of side effects. Clinicians should take all known safety and compliance of patients into account when choosing an optimal strategy. Since sample size of included studies, further RCTs are strongly encouraged to address the clinical question.
Keywords: network meta-analysis; phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors; ureteral calculi.
© 2019 The Authors. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors for the treatment of distal ureteral calculi: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Investig Clin Urol. 2017 Mar;58(2):82-89. doi: 10.4111/icu.2017.58.2.82. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Investig Clin Urol. 2017. PMID: 28261676 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Is silodosin better than tadalafil as a medical expulsive therapy in lower ureter stones?Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):13642. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.13642. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40247733
Cited by
-
Efficacy of tamsulosin versus tadalafil as medical expulsive therapy on stone expulsion in patients with distal ureteral stones: A randomized double-blind clinical trial.Int Braz J Urol. 2021 Sep-Oct;47(5):982-988. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.1007. Int Braz J Urol. 2021. PMID: 34260175 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of the combination of tadalafil and tamsulosin versus tadalafil alone as a medical expulsive therapy for stone L1/3 ureter 10 mm or less: A prospective comparative placebo-controlled study.Curr Urol. 2024 Dec;18(4):278-282. doi: 10.1097/CU9.0000000000000206. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Curr Urol. 2024. PMID: 40256299 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing efficacy and safety of monotherapy and combination therapy with tadalafil, tamsulosin, and silodosin for distal ureteral stones: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Asian J Urol. 2025 Apr;12(2):189-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2024.05.003. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Asian J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40458580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Silodosin and Tadalafil monotherapy versus combination of both drugs as MET for distal ureteric stones: A prospective, double blinded, randomized clinical trial.Arab J Urol. 2024 Sep 16;23(2):124-130. doi: 10.1080/20905998.2024.2403274. eCollection 2025. Arab J Urol. 2024. PMID: 40182572 Free PMC article.
-
Pooled-analysis of tadalafil and tamsulosin for ureteral calculi.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 30;15:1351312. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1351312. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38873423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Turk C, Petrik A, Sarica K, Seiz C, Skolarikos A, Straub M, et al. EAU guidelines on interventional treatment for urolithiasis. Eur Urol. 2016;69(3):475–482. - PubMed
-
- Furyk JS, Chu K, Banks C, Greenslade J, Keijzers J, Thom O, et al. Distal ureteric stones and tamsulosin: A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized, multicenter trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2016;67(1):86–95. - PubMed
-
- Miller OF , Kane CJ. Time to stone passage for observed ureteral calculi: A guide for patient education. J Urol. 1999;162(3 Pt 1):688–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

