Routine versus Targeted Viral Load Strategy among Patients Starting Antiretroviral in Hanoi, Vietnam
- PMID: 30897303
- PMCID: PMC6428502
- DOI: 10.1002/jia2.25258
Routine versus Targeted Viral Load Strategy among Patients Starting Antiretroviral in Hanoi, Vietnam
Abstract
Introduction: HIV viral load (VL) testing is recommended by the WHO as the preferred method for monitoring patients on antiretroviral therapy (ART). However, evidence that routine VL (RVL) monitoring improves clinical outcomes is lacking.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, randomized controlled trial of RVL monitoring every six months versus a targeted VL (TVL) strategy (routine CD4 plus VL testing if clinical or immunological failure) in patients starting ART between April 2011 and April 2014 at Bach Mai Hospital in Hanoi. Six hundred and forty-seven subjects were randomized to RVL (n = 305) or TVL monitoring (n = 342) and followed up for three years. Primary endpoints were death or WHO clinical Stage 4 events between six and thirty-six months of ART and rate of virological suppression at three years.
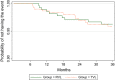
Results: Overall, 37.1% of subjects were female, median age was 33.4 years (IQR: 29.5 to 38.6), and 47% had a CD4 count ≤100 cells/mm3 at time of ART initiation. Approximately 44% of study events (death, LTFU, withdrawal, or Stage 4 event) and 68% of deaths occurred within the first six months of ART. Among patients on ART at six months, death or Stage 4 event occurred in 3.6% of RVL and 3.9% of TVL (p = 0.823). Survival analysis showed no significant difference between the groups (p = 0.825). Viral suppression at 36 months of ART was 97.2% in RVL and 98.9% in TVL (p = 0.206) at a threshold of 400 copies/mL and was 98.0% in RVL and 98.9% in TVL (p = 0.488) at 1000 copies/mL. In ITT analysis, 20.7% in RVL and 21.9% in TVL (p = 0.693) were unsuppressed at 1000 copies/mL.
Conclusions: We found no significant difference in rates of death or Stage 4 events and virological failure in patients with RVL monitoring compared to those monitored with a TVL strategy after three years of follow-up. Viral suppression rates were high overall and there were few study events among patients alive and on ART after six months, limiting the study's power to detect a difference among study arms. Nonetheless, these data suggest that the choice of VL monitoring strategy may have less impact on patient outcomes compared to efforts to reduce early mortality and improve ART retention.
Keywords: ART; HIV; Vietnam; monitoring; randomized controlled trial; viral load.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of the International AIDS Society published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the International AIDS Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of peer support on virologic failure in HIV-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy - a cluster randomized controlled trial in Vietnam.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Dec 16;16(1):759. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-2017-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27986077 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adoption of routine virologic testing and predictors of virologic failure among HIV-infected children on antiretroviral treatment in western Kenya.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 9;13(11):e0200242. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200242. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30412576 Free PMC article.
-
Switching HIV treatment in adults based on CD4 count versus viral load monitoring: a randomized, non-inferiority trial in Thailand.PLoS Med. 2013 Aug;10(8):e1001494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001494. Epub 2013 Aug 6. PLoS Med. 2013. PMID: 23940461 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The impact of analytical treatment interruptions and trial interventions on time to viral re-suppression in people living with HIV restarting ART in cure-related clinical studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Int AIDS Soc. 2024 Aug;27(8):e26349. doi: 10.1002/jia2.26349. J Int AIDS Soc. 2024. PMID: 39155436 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Low CD4 Cell Counts and High Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Viral Load to the Efficacy of Preferred First-Line Antiretroviral Regimens for Treating HIV Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Jun 8;76(11):2027-2037. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciad177. Clin Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36975712
Cited by
-
The Cost-Effectiveness of Adapting and Implementing a Brief Intervention to Target Frequent Alcohol Use Among Persons with HIV in Vietnam.AIDS Behav. 2021 Jul;25(7):2108-2119. doi: 10.1007/s10461-020-03139-y. Epub 2021 Jan 3. AIDS Behav. 2021. PMID: 33392969 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Virological failure and treatment switch after ART initiation among people living with HIV with and without routine viral load monitoring in Asia.J Int AIDS Soc. 2022 Aug;25(8):e25989. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25989. J Int AIDS Soc. 2022. PMID: 36028921 Free PMC article.
-
Performance and Outcomes of Routine Viral Load Testing in People Living with HIV Newly Initiating ART in the Integrated HIV Care Program in Myanmar between January 2016 and December 2017.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2020 Aug 31;5(3):140. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed5030140. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32878307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection – recommendations for a public health approach. 2016. - PubMed
-
- Moore DM, Awor A, Downing R, Kaplan J, Montaner JSG, Hancock J, et al. CD4+ T‐cell count monitoring does not accurately identify HIV‐infected adults with virologic failure receiving antiretroviral therapy. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2008;49:477–84. - PubMed
-
- Mee P, Fielding KL, Charalambous S, Churchyard GJ, Grant AD. Evaluation of the WHO criteria for antiretroviral treatment failure among adults in South Africa. AIDS. 2008;22:1971–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous