Extracytoplasmic Function σ Factors Can Be Implemented as Robust Heterologous Genetic Switches in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 30897511
- PMCID: PMC6426705
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.03.001
Extracytoplasmic Function σ Factors Can Be Implemented as Robust Heterologous Genetic Switches in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
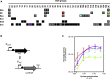
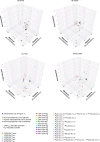
In bacteria, the promoter specificity of RNA polymerase is determined by interchangeable σ subunits. Extracytoplasmic function σ factors (ECFs) form the largest and most diverse family of alternative σ factors, and their suitability for constructing genetic switches and circuits was already demonstrated. However, a systematic study on how genetically determined perturbations affect the behavior of these switches is still lacking, which impairs our ability to predict their behavior in complex circuitry. Here, we implemented four ECF switches in Bacillus subtilis and comprehensively characterized their robustness toward genetic perturbations, including changes in copy number, protein stability, or antisense transcription. All switches show characteristic dose-response behavior that varies depending on the individual ECF-promoter pair. Most perturbations had performance costs. Although some general design rules could be derived, a detailed characterization of each ECF switch before implementation is recommended to understand and thereby accommodate its individual behavior.
Keywords: Biological Sciences; Biotechnology; Microbiology; Molecular Biology.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Annunziata F., Matyjaszkiewicz A., Fiore G., Grierson C.S., Marucci L., di Bernardo M., Savery N.J. An orthogonal multi-input integration system to control gene expression in Escherichia coli. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017;6:1816–1824. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

