Histone deacetylase enzymes as potential drug targets of Neglected Tropical Diseases caused by cestodes
- PMID: 30897528
- PMCID: PMC6426703
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2019.02.003
Histone deacetylase enzymes as potential drug targets of Neglected Tropical Diseases caused by cestodes
Abstract
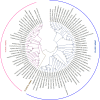
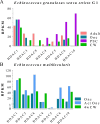
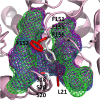
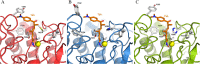
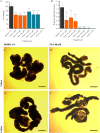
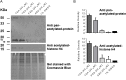
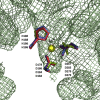
Cestode parasites cause neglected diseases, such as echinococcosis and cysticercosis, which represent a significant problem in human and animal health. Benzimidazoles and praziquantel are the only available drugs for chemotherapy and it is therefore important to identify new alternative drugs against cestode parasites. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are validated drug targets for the treatment of cancer and other diseases, including neglected diseases. However, knowledge of HDACs in cestodes is very scarce. In this work, we investigated cestode HDACs as potential drug targets to develop new therapies against neglected diseases caused by cestodes. Here we showed the full repertoire of HDAC coding genes in several members of the class Cestoda. Between 6 and 7 zinc-dependent HDAC coding genes were identified in the genomes of species from Echinococcus, Taenia, Mesocestoides and Hymenolepis genera. We classified them as Class I and II HDACs and analyzed their transcriptional expression levels throughout developmental stages of Echinococcus spp. We confirmed for the first time the complete HDAC8 nucleotide sequences from Echinococcus canadensis G7 and Mesocestoides corti. Homology models for these proteins showed particular structural features which differentiate them from HDAC8 from Homo sapiens. Furthermore, we showed that Trichostatin A (TSA), a pan-HDAC inhibitor, decreases the viability of M. corti, alters its tegument and morphology and produces an increment of the total amount of acetylated proteins, including acetylated histone H4. These results suggest that HDAC from cestodes are functional and might play important roles on survival and development. The particular structural features observed in cestode HDAC8 proteins suggest that these enzymes could be selectively targeted. This report provides the basis for further studies on cestode HDAC enzymes and for discovery of new HDAC inhibitors for the treatment of neglected diseases caused by cestode parasites.
Keywords: Cestode; Echinococcus; Histone deacetylases; Mesocestoides corti; Neglected Tropical Diseases; Trichostatin A.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The potential for histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors as cestocidal drugs.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Mar 3;15(3):e0009226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009226. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 33657105 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of sirtuin enzymes in cestodes and evaluation of sirtuin inhibitors as new cestocidal molecules.Int J Parasitol. 2022 Apr;52(5):317-329. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2021.12.002. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Int J Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35150663
-
Extracts and Terpenoids from Stevia Species as Potential Anthelmintics for Neglected Tropical Diseases Caused by Cestode Parasites.Molecules. 2024 Sep 18;29(18):4430. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184430. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339424 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Based Inhibitor Discovery of Class I Histone Deacetylases (HDACs).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 22;21(22):8828. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228828. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33266366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc-dependent histone deacetylases: Potential therapeutic targets for arterial hypertension.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Aug;202:115111. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115111. Epub 2022 May 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35640713 Review.
Cited by
-
Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors for the Treatment of Schistosomiasis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 10;15(1):80. doi: 10.3390/ph15010080. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35056137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trickle infection with Heligmosomoides polygyrus results in decreased worm burdens but increased intestinal inflammation and scarring.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 8;13:1020056. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1020056. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36569914 Free PMC article.
-
The potential for histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors as cestocidal drugs.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Mar 3;15(3):e0009226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009226. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 33657105 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological Role of HDAC8: Cancer and Beyond.Cells. 2022 Oct 9;11(19):3161. doi: 10.3390/cells11193161. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cestode strobilation: prediction of developmental genes and pathways.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jul 16;21(1):487. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06878-3. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32677885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avila H.G., Santos G.B., Cucher M.A., Macchiaroli N., Pérez M.G., Baldi G., Jensen O., Pérez V., López R., Negro P., Scialfa E., Zaha A., Ferreira H.B., Rosenzvit M., Kamenetzky L. Implementation of new tools in molecular epidemiology studies of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato in South America. Parasitol. Int. 2017;66:250–257. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2017.02.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berriman M., Haas B.J., LoVerde P.T., Wilson R.A., Dillon G.P., Cerqueira G.C., Mashiyama S.T., Al-Lazikani B., Andrade L.F., Ashton P.D., Aslett M.A., Bartholomeu D.C., Blandin G., Caffrey C.R., Coghlan A., Coulson R., Day T.A., Delcher A., DeMarco R., Djikeng A., Eyre T., Gamble J.A., Ghedin E., Gu Y., Hertz-Fowler C., Hirai H., Hirai Y., Houston R., Ivens A., Johnston D.A., Lacerda D., Macedo C.D., McVeigh P., Ning Z., Oliveira G., Overington J.P., Parkhill J., Pertea M., Pierce R.J., Protasio A.V., Quail M.A., Rajandream M.-A., Rogers J., Sajid M., Salzberg S.L., Stanke M., Tivey A.R., White O., Williams D.L., Wortman J., Wu W., Zamanian M., Zerlotini A., Fraser-Liggett C.M., Barrell B.G., El-Sayed N.M. The genome of the blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni. Nature. 2009;460:352–358. doi: 10.1038/nature08160. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

