Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Recognition of Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles (NANPs) in Human Primary Blood Cells
- PMID: 30897721
- PMCID: PMC6470694
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24061094
Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Recognition of Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles (NANPs) in Human Primary Blood Cells
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Hong, E., et al. Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Recognition of Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles (NANPs) in Human Primary Blood Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 1094.Molecules. 2019 Oct 25;24(21):3852. doi: 10.3390/molecules24213852. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31731534 Free PMC article.
Abstract
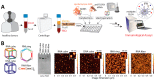
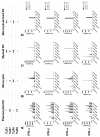
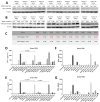
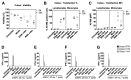
Infusion reactions (IRs) create a translational hurdle for many novel therapeutics, including those utilizing nanotechnology. Nucleic acid nanoparticles (NANPs) are a novel class of therapeutics prepared by rational design of relatively short oligonucleotides to self-assemble into various programmable geometric shapes. While cytokine storm, a common type of IR, has halted clinical development of several therapeutic oligonucleotides, NANP technologies hold tremendous potential to bring these reactions under control by tuning the particle's physicochemical properties to the desired type and magnitude of the immune response. Recently, we reported the very first comprehensive study of the structure⁻activity relationship between NANPs' shape, size, composition, and their immunorecognition in human cells, and identified the phagolysosomal pathway as the major route for the NANPs' uptake and subsequent immunostimulation. Here, we explore the molecular mechanism of NANPs' recognition by primary immune cells, and particularly the contributing role of the Toll-like receptors. Our current study expands the understanding of the immune recognition of engineered nucleic acid-based therapeutics and contributes to the improvement of the nanomedicine safety profile.
Keywords: NANPs; Toll-like receptors; immunotoxicity; infusion reaction; interferon; nanoparticles; nucleic acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Recognition of and Reactions to Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles by Human Immune Cells.Molecules. 2021 Jul 12;26(14):4231. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144231. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and Composition Define Immunorecognition of Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles.Nano Lett. 2018 Jul 11;18(7):4309-4321. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b01283. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Nano Lett. 2018. PMID: 29894623 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleic acid nanoparticles (NANPs) as molecular tools to direct desirable and avoid undesirable immunological effects.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Jun;173:427-438. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.04.011. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 33857556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of Cytokines by Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles (NANPs) Depends on the Type of Delivery Carrier.Molecules. 2021 Jan 27;26(3):652. doi: 10.3390/molecules26030652. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33513786 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Generations of PAMAM Dendrimers and Compositions of Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles Govern Delivery and Immune Recognition.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025 Jun 9;11(6):3726-3737. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5c00336. Epub 2025 May 20. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025. PMID: 40391736 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic immunomodulation by rationally designed nucleic acids and nucleic acid nanoparticles.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 31;14:1053550. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1053550. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36798121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) Combined with SAXS-Driven Molecular Dynamics for Structural Analysis of Multistranded RNA Assemblies.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Dec 11;16(49):67178-67191. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c12397. Epub 2024 Nov 26. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39593218 Free PMC article.
-
Biomotors, viral assembly, and RNA nanobiotechnology: Current achievements and future directions.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Nov 11;20:6120-6137. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.11.007. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36420155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges to optimizing RNA nanostructures for large scale production and controlled therapeutic properties.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2020 May 26;15(13):1331-40. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2020-0034. Online ahead of print. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32452262 Free PMC article.
-
Immunostimulation of Fibrous Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles Can be Modulated through Aptamer-Based Functional Moieties: Unveiling the Structure-Activity Relationship and Mechanistic Insights.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Feb 21;16(7):8430-8441. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c17779. Epub 2024 Feb 12. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38344840 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

