Nanoparticles for Bioapplications: Study of the Cytotoxicity of Water Dispersible CdSe(S) and CdSe(S)/ZnO Quantum Dots
- PMID: 30897752
- PMCID: PMC6474084
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9030465
Nanoparticles for Bioapplications: Study of the Cytotoxicity of Water Dispersible CdSe(S) and CdSe(S)/ZnO Quantum Dots
Abstract
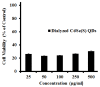
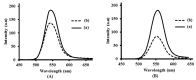
Semiconductor nanocrystals or quantum dots (QDs) have unique optical and physical properties that make them potential imaging tools in biological and medical applications. However, concerns over the aqueous dispersivity, toxicity to cells, and stability in biological environments may limit the use of QDs in such applications. Here, we report an investigation into the cytotoxicity of aqueously dispersed CdSe(S) and CdSe(S)/ZnO core/shell QDs in the presence of human colorectal carcinoma cells (HCT-116) and a human skin fibroblast cell line (WS1). The cytotoxicity of the precursor solutions used in the synthesis of the CdSe(S) QDs was also determined in the presence of HCT-116 cells. CdSe(S) QDs were found to have a low toxicity at concentrations up to 100 µg/mL, with a decreased cell viability at higher concentrations, indicating a highly dose-dependent response. Meanwhile, CdSe(S)/ZnO core/shell QDs exhibited lower toxicity than uncoated QDs at higher concentrations. Confocal microscopy images of HCT-116 cells after incubation with CdSe(S) and CdSe(S)/ZnO QDs showed that the cells were stable in aqueous concentrations of 100 µg of QDs per mL, with no sign of cell necrosis, confirming the cytotoxicity data.
Keywords: HCT-116; WS1; aqueous synthesis; bioapplications of QDs; core/shell QDs; in vitro cytotoxicity of QDs; water dispersive QDs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they hold no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Investigation of biocompatible and protein sensitive highly luminescent quantum dots/nanocrystals of CdSe, CdSe/ZnS and CdSe/CdS.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2017 May 15;179:201-210. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2017.02.028. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2017. PMID: 28242450
-
Hydrothermal synthesis of highly luminescent blue-emitting ZnSe(S) quantum dots exhibiting low toxicity.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016 Jul 1;64:167-172. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.03.061. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016. PMID: 27127041
-
Design and synthesis of highly luminescent near-infrared-emitting water-soluble CdTe/CdSe/ZnS core/shell/shell quantum dots.Inorg Chem. 2009 Oct 19;48(20):9723-31. doi: 10.1021/ic9010949. Inorg Chem. 2009. PMID: 19772326
-
CdTe and CdSe quantum dots cytotoxicity: a comparative study on microorganisms.Sensors (Basel). 2011;11(12):11664-78. doi: 10.3390/s111211664. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Sensors (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22247686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cytotoxicity of cadmium-based quantum dots.Biomaterials. 2012 Feb;33(5):1238-44. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.10.070. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Biomaterials. 2012. PMID: 22078811 Review.
Cited by
-
Green Synthesis of Engineered CdS Nanoparticles with Reduced Cytotoxicity for Enhanced Bioimaging Application.ACS Omega. 2021 Mar 17;6(12):8646-8655. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00519. eCollection 2021 Mar 30. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33817526 Free PMC article.
-
MOF-Derived Porous Fe2O3 Nanoparticles Coupled with CdS Quantum Dots for Degradation of Bisphenol A under Visible Light Irradiation.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Aug 29;10(9):1701. doi: 10.3390/nano10091701. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32872400 Free PMC article.
-
Current Strategies and Potential Prospects for Nanoparticle-Mediated Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022 Aug 31;15:2653-2673. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S380550. eCollection 2022. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022. PMID: 36068795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Lysosome-Targetable Fluorescence Probe Based on L-Cysteine-Polyamine-Morpholine-Modified Quantum Dots for Imaging in Living Cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Mar 9;15:1611-1622. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S234927. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32210555 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Expression Profiling of the Liver and Lung in Mice After Exposure to ZnO Quantum Dots.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Apr 28;15:2947-2955. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S246754. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32425526 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

