Chromatographic Analysis and Anti-Oxidative Property of Naoxinqing Tablet, a Proprietary Preparation of Diospyros Kaki Leaves
- PMID: 30897753
- PMCID: PMC6470564
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24061101
Chromatographic Analysis and Anti-Oxidative Property of Naoxinqing Tablet, a Proprietary Preparation of Diospyros Kaki Leaves
Abstract
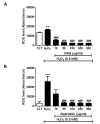
The Naoxinqing (NXQ) tablet is a standardised proprietary herbal product containing an extract of persimmon leaves (Diospyros kaki) for the management of cardio- and cerebrovascular diseases. Although previous reports suggested that the efficacy of NXQ is at least partly mediated by its anti-oxidative property, the anti-oxidative effect of the major components of NXQ has not been studied systematically. For quality control purposes, only analytical methods limited to 3 marker analytes have been reported, the extent to which the other components affect efficacy has not been explored. In this study, we developed an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC MS/MS) method for the identification of seven analytes (kaempferol-3-O-glucoside (astragalin), quercetin-3-O-galactoside (hypericin), quercetin-3-O-glucoside (isoquercitin), kaempferol, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (protocatechuic acid), and furan-2-carboxylic acid (pyromucic acid) and quercetin) in the NXQ. This is the first method reported and validated for the quantification of the seven major secondary metabolites in NXQ. The results for the quantified analytes were then compared in 15 different batches of NXQ. The variation observed in the seven components highlights the need to quantify key bioactive components to ensure product consistency. Radical scavenging activity and abundance was used to rank the analytes. The anti-oxidative effects of NXQ were examined using cultured human vascular endothelial cells (EA.hy926). Corrected 2,2-di(4-tert-octylphenyl)-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) activity results revealed that quercetin and kaempferol have the strongest anti-oxidant capacity in the extract. Both quercetin and kaempferol significantly inhibited the hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂)-induced EA.hy926 cell injury and intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. In conclusion, we established and validated an UPLC-MS/MC method for the analysis of major bioactive components in the NXQ and demonstrated that its anti-oxidative property may play a critical role in cerebrovascular protection.
Keywords: Naoxinqing; UPLC MS/MC analysis; anti-oxidative; endothelial cells; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
As a medical research institute, NICM Health Research Institute receives research grants and donations from foundations, universities, government agencies, individuals and industry. Sponsors and donors also provide untied funding for work to advance the vision and mission of the Institute. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simultaneous quantitative analysis of 11 flavonoid derivatives with a single marker in persimmon leaf extraction and evaluation of their myocardium protection activity.J Nat Med. 2019 Mar;73(2):404-418. doi: 10.1007/s11418-018-1274-y. Epub 2019 Jan 1. J Nat Med. 2019. PMID: 30600429
-
Method Development and Validation for Simultaneous Determination of Six Flavonoids in Rat Eyes after Oral Administration of Diospyros kaki Leaves Extract by UPLC-MS/MS.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2021 Feb 1;69(2):218-221. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c20-00562. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2021. PMID: 33268666
-
Deastringent Peel Extracts of Persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb. cv. Cheongdo-Bansi) Protect Neuronal PC-12 and SH-SY5Y Cells against Oxidative Stress.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Jul 28;28(7):1094-1104. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1801.01013. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29975999
-
Persimmon (Diospyros kaki L.) leaves: a review on traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Apr 2;163:229-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.007. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25637828 Review.
-
A Review: Pharmacological Effect of Natural Compounds in Diospyros kaki Leaves from the Perspective of Oxidative Stress.Molecules. 2023 Dec 30;29(1):215. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010215. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Antioxidant Capacities of Natural Products 2019.Molecules. 2020 Dec 1;25(23):5676. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235676. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33271992 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling of chemical constituents of Matricarla chamomilla L. by UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS and in vivo evaluation its anti-asthmatic activity.Heliyon. 2023 Apr 24;9(5):e15470. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15470. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37153405 Free PMC article.
-
Persimmon Leaves: Nutritional, Pharmaceutical, and Industrial Potential-A Review.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 18;12(4):937. doi: 10.3390/plants12040937. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insecticidal Activities of Atriplex halimus L., Salvia rosmarinus Spenn. and Cuminum cyminum L. against Dactylopius opuntiae (Cockerell) under Laboratory and Greenhouse Conditions.Insects. 2022 Oct 13;13(10):930. doi: 10.3390/insects13100930. Insects. 2022. PMID: 36292878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mozaffarian D., Benjamin E.J., Go A.S., Arnett D.K., Blaha M.J., Cushman M., Das S.R., de Ferranti S., Després J.P., Fullerton H.J., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133:e38–e48. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000350. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

