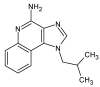
In Vitro Enhanced Skin Permeation and Retention of Imiquimod Loaded in β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponge Hydrogel
- PMID: 30897794
- PMCID: PMC6471382
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11030138
In Vitro Enhanced Skin Permeation and Retention of Imiquimod Loaded in β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponge Hydrogel
Abstract
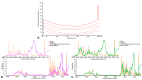
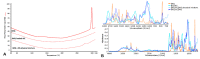
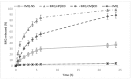
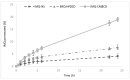
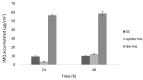
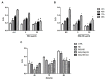
Imiquimod (IMQ) is an immune response modifier clinically used for the treatment of various topical diseases. However, its poor aqueous solubility and skin penetration capability make the topical delivery of IMQ a challenging task. This work aims at developing a nanomedicine-based topical formulation, carrying IMQ to control the scarring process for the treatment of aberrant wounds. For this purpose, IMQ was loaded in β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges and dispersed in a hydrogel suitable for dermal application. The formulation was characterized in vitro and compared with IMQ inclusion complexes, with (2-hydroxy)propyl β-cyclodextrin(HPβCD) and carboxymethyl β-cyclodextrin (CMβCD) showing enhanced penetration properties. The hydrogel containing IMQ-loaded nanosponges could act as a drug reservoir and guarantee the sustained release of IMQ through the skin. A greater inhibitory effect on fibroblast proliferation was observed for IMQ loaded in nanosponges compared to the other formulations.
Keywords: controlled release; cyclodextrins; imiquimod; inclusion complex; nanosponges.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ester-Based Hydrophilic Cyclodextrin Nanosponges for Topical Ocular Drug Delivery.Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(46):6988-6997. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161216113207. Curr Pharm Des. 2016. PMID: 27981908
-
Formulation Development, In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Topical Hydrogel Formulation of Econazole Nitrate-Loaded β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges.J Pharm Sci. 2021 Nov;110(11):3702-3714. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2021.07.008. Epub 2021 Jul 20. J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34293406
-
Development and Evaluation of Hydrogel-Based Sulfasalazine-Loaded Nanosponges for Enhanced Topical Psoriasis Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 10;18(3):391. doi: 10.3390/ph18030391. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143167 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclodextrin based nanosponges for pharmaceutical use: a review.Acta Pharm. 2013 Sep;63(3):335-58. doi: 10.2478/acph-2013-0021. Acta Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24152895 Review.
-
Evolving Era of "Sponges": Nanosponges as a Versatile Nanocarrier for the Effective Skin Delivery of Drugs.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(23):1885-1896. doi: 10.2174/1381612828666220518090431. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 35585809 Review.
Cited by
-
Formulation and Evaluation of Transdermal Patches Containing BGP-15.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 27;16(1):36. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010036. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38258047 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges: Overview and Opportunities.Front Chem. 2022 Mar 24;10:859406. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.859406. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35402388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Solubility, Cytotoxicity and Photostability Studies of Resveratrol and Oxyresveratrol Loaded Nanosponges.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Oct 20;11(10):545. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11100545. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31635183 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges as Drug Delivery Systems: Understanding the Physicochemical Factors Influencing Drug Loading and Release Kinetics.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 20;25(6):3527. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063527. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges Inclusion Compounds Associated with Silver Nanoparticles to Increase the Antimicrobial Activity of Quercetin.Materials (Basel). 2023 May 5;16(9):3538. doi: 10.3390/ma16093538. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37176420 Free PMC article.

