Inhibition of Mitochondrial Complex Function-The Hepatotoxicity Mechanism of Emodin Based on Quantitative Proteomic Analyses
- PMID: 30897821
- PMCID: PMC6468815
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8030263
Inhibition of Mitochondrial Complex Function-The Hepatotoxicity Mechanism of Emodin Based on Quantitative Proteomic Analyses
Abstract
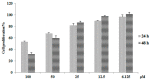
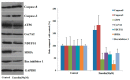
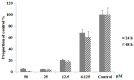
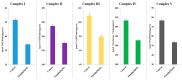
Emodin is the main component of traditional Chinese medicines including rhubarb, Polygonum multiflorum, and Polygonum cuspidatum. It has confirmed hepatotoxicity and may be the main causative agent of liver damage associated with the above-mentioned traditional Chinese medicines. However, current research does not explain the mechanism of emodin in hepatotoxicity. In this study, L02 cells were used as a model to study the mechanism of emodin-induced hepatocyte apoptosis using quantitative proteomics, and the results were verified by Western blot. A total of 662 differentially expressed proteins were discovered and analyzed using Gene Ontology (GO) and pathway enrichment analysis. The results show that the oxidative phosphorylation pathway is highly represented. Abnormalities in this pathway result in impaired mitochondrial function and represent mitochondrial damage. This result is consistent with mitochondria membrane potential measurements. Analysis of differentially expressed proteins revealed that emodin mainly affects oxidative phosphorylation pathways by inhibiting the function of the mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes; the mitochondrial respiratory chain complex activity assay result also confirmed that emodin could inhibit the activity of all mitochondrial complexes. This results in an increase in caspase-3, a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP,) an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS), and disorders in ATP synthesis, etc., eventually leading to mitochondrial damage and hepatocyte apoptosis in vitro.
Keywords: complex; emodin; hepatotoxicity; mitochondrial; proteomic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Hepatotoxicity and mechanism study of chrysophanol-8-O-glucoside in vitro.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Dec;120:109531. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109531. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31648163
-
The evaluation and molecular mechanisms of hepatotoxicity induced by trans-emodin dianthrones isolated from Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. in vitro.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 May 28;348:119916. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119916. Epub 2025 May 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40319934
-
Aloe-emodin Induces Apoptosis in Human Liver HL-7702 Cells through Fas Death Pathway and the Mitochondrial Pathway by Generating Reactive Oxygen Species.Phytother Res. 2017 Jun;31(6):927-936. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5820. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Phytother Res. 2017. PMID: 28444790
-
Emodin in cardiovascular disease: The role and therapeutic potential.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 23;13:1070567. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1070567. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36618923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the pharmacological effects and molecular mechanisms of emodin in the treatment of metabolic diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 31;14:1240820. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1240820. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38027005 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Herb-Induced Liver Injury: Phylogenetic Relationship, Structure-Toxicity Relationship, and Herb-Ingredient Network Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 25;20(15):3633. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153633. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31349548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Emodin for Gastrointestinal Cancers.Integr Cancer Ther. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15347354211067469. doi: 10.1177/15347354211067469. Integr Cancer Ther. 2022. PMID: 34984952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qingluo Tongbi Formula Alleviates Hepatotoxicity Induced by Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. F. by Regulating Excessive Mitophagy Through the PERK-ATF4 Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 7;13:918466. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.918466. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35873540 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatotoxic metabolites in Polygoni Multiflori Radix- Comparative toxicology in mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 11;13:1007284. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1007284. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36304159 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the mechanism of emodin-induced hepatotoxicity.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 25;10(13):e33631. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33631. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39027614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang Y.X., Li J.S., Peng W.W., Liu X., Yang G.M., Chen L.H., Cai B.C. Comparative pharmacokinetics of aloe-emodin, rhein and emodin determined by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry after oral administration of a rhubarb peony decoction and rhubarb extract to rats. Pharmazie. 2013;68:333–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

