Lipoprotein(a) Particle Production as a Determinant of Plasma Lipoprotein(a) Concentration Across Varying Apolipoprotein(a) Isoform Sizes and Background Cholesterol-Lowering Therapy
- PMID: 30897995
- PMCID: PMC6509712
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011781
Lipoprotein(a) Particle Production as a Determinant of Plasma Lipoprotein(a) Concentration Across Varying Apolipoprotein(a) Isoform Sizes and Background Cholesterol-Lowering Therapy
Abstract
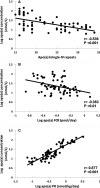
Background Elevated lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)), a low-density lipoprotein-like particle bound to the polymorphic apolipoprotein(a) (apo(a)), may be causal for cardiovascular disease. However, the metabolism of Lp(a) in humans is poorly understood. Methods and Results We investigated the kinetics of Lp(a)-apo(a) and low-density lipoprotein-apoB-100 in 63 normolipidemic men. The fractional catabolic rate ( FCR ) and production rate PR ) were studied. Plasma apo(a) concentration was significantly and inversely associated with apo(a) isoform size ( r=-0.536, P<0.001) and apo(a) FCR ( r=-0.363, P<0.01), and positively with apo(a) PR ( r=0.877, P<0.001). There were no significant associations between the FCR s of apo(a) and low-density lipoprotein-apoB-100. Subjects with smaller apo(a) isoform sizes (≤22 kringle IV repeats) had significantly higher apo(a) PR ( P<0.05) and lower apo(a) FCR ( P<0.01) than those with larger sizes. Plasma apo(a) concentration was significantly associated with apo(a) PR ( r=0.930, P<0.001), but not with FCR ( r=-0.012, P>0.05) in subjects with smaller apo(a) isoform size. In contrast, both apo(a) PR and FCR were significantly associated with plasma apo(a) concentrations ( r=0.744 and -0.389, respectively, P<0.05) in subjects with larger isoforms. In multiple regression analysis, apo(a) PR and apo(a) isoform size were significant predictors of plasma apo(a) concentration independent of low-density lipoprotein-apoB-100 FCR and background therapy with atorvastatin and evolocumab. Conclusions In normolipidemic men, the plasma Lp(a) concentration is predominantly determined by the rate of production of Lp(a) particles, irrespective of apo(a) isoform size and background therapy with a statin and a proprotein convertase subtilisin-kexin type 9 inhibitor. Our findings underscore the importance of therapeutic targeting of the hepatic synthesis and secretion of Lp(a) particles. Lp(a) particle catabolism may only play a modest role in determining Lp(a) concentration in subjects with larger apo(a) isoform size. Clinical Trial Registration URL : http://www.clinicaltrials.gov . Unique identifier: NCT 02189837.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02189837.
Keywords: apolipoprotein; cardiovascular disease risk factors; cholesterol‐lowering drugs; lipids and lipoprotein metabolism; low‐density lipoprotein.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Controlled study of the effect of proprotein convertase subtilisin-kexin type 9 inhibition with evolocumab on lipoprotein(a) particle kinetics.Eur Heart J. 2018 Jul 14;39(27):2577-2585. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy122. Eur Heart J. 2018. PMID: 29566128
-
PCSK9 Inhibition with alirocumab increases the catabolism of lipoprotein(a) particles in statin-treated patients with elevated lipoprotein(a).Metabolism. 2020 Jun;107:154221. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154221. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Metabolism. 2020. PMID: 32240727
-
Relationship of apolipoprotein(a) isoform size with clearance and production of lipoprotein(a) in a diverse cohort.J Lipid Res. 2023 Mar;64(3):100336. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2023.100336. Epub 2023 Jan 24. J Lipid Res. 2023. PMID: 36706955 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein(a), cardiovascular disease, and contemporary management.Mayo Clin Proc. 2013 Nov;88(11):1294-311. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.09.003. Mayo Clin Proc. 2013. PMID: 24182706 Review.
-
Recent advances in demystifying the metabolism of lipoprotein(a).Atherosclerosis. 2022 May;349:82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.04.002. Atherosclerosis. 2022. PMID: 35606080 Review.
Cited by
-
Sortilin enhances secretion of apolipoprotein(a) through effects on apolipoprotein B secretion and promotes uptake of lipoprotein(a).J Lipid Res. 2022 Jun;63(6):100216. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2022.100216. Epub 2022 Apr 22. J Lipid Res. 2022. PMID: 35469919 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in lipoprotein(a) response to potent lipid lowering: The role of apolipoprotein (a) isoform size.J Clin Lipidol. 2025 Jan-Feb;19(1):39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2024.11.008. Epub 2024 Dec 4. J Clin Lipidol. 2025. PMID: 39828454
-
Relationship between carotid atherosclerosis and lipoprotein (a) in patients with acute ischemic stroke.Front Neurol. 2024 Jun 26;15:1383771. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1383771. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38988596 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein(a) in Cardiovascular Diseases: Insight From a Bibliometric Study.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 5;10:923797. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.923797. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35865239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Apolipoprotein(a) Isoform Size Using Phenotypic and Genotypic Methods.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 9;24(18):13886. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813886. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Danesh J, Collins R, Peto R. Lipoprotein(a) and coronary heart disease. Meta‐analysis of prospective studies. Circulation. 2000;102:1082–1085. - PubMed
-
- Kamstrup PR, Tybjaerg‐Hansen A, Nordestgaard BG. Extreme lipoprotein(a) levels and improved cardiovascular risk prediction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:1146–1156. - PubMed
-
- Saleheen D, Haycock PC, Zhao W, Rasheed A, Taleb A, Imran A, Abbas S, Majeed F, Akhtar S, Qamar N, Zaman KS, Yaqoob Z, Saghir T, Rizvi SNH, Memon A, Mallick NH, Ishaq M, Rasheed SZ, Memon FU, Mahmood K, Ahmed N, Frossard P, Tsimikas S, Witztum JL, Marcovina S, Sandhu M, Rader DJ, Danesh J. Apolipoprotein(a) isoform size, lipoprotein(a) concentration, and coronary artery disease: a Mendelian randomisation analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:524–533. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

