Effectiveness and Safety of Platelet ADP -P2Y12 Receptor Inhibitors Influenced by Smoking Status: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 30898054
- PMCID: PMC6509729
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.010889
Effectiveness and Safety of Platelet ADP -P2Y12 Receptor Inhibitors Influenced by Smoking Status: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
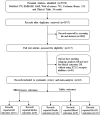
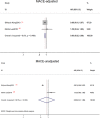
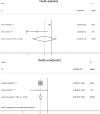
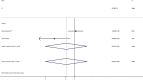
Background As reports on the influence of cigarette smoking, an important cardiovascular risk factor, on platelet ADP -P2Y12 receptor inhibitors lack consistency, we aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of platelet ADP -P2Y12 receptor inhibitors influenced by smoking status. Methods and Results PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE , Clinical Trials, and the Cochrane Library were searched from inception until June 2018. Among the 5076 citations retrieved, 22 studies, including 163 011 patients with or without percutaneous coronary intervention, were included for meta-analysis. Compared with nonsmokers within the first year of follow-up, the reductions of stroke and major adverse cardiovascular event rate were 18% ( P=0.008) and 26% ( P=0.02), respectively. A 20% reduction in stroke ( P=0.02) and a 34% reduction in major adverse cardiovascular event ( P=0.0001) rates were observed in smoking patients without percutaneous coronary intervention. No significant difference was observed in clinical outcome rates among prasugrel, ticagrelor, and clopidogrel in different smoking status. No significant difference was found in myocardial infarction and bleeding event incidence between current smokers and nonsmokers. Conclusions We concluded that current smokers had a lower incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events and stroke events than did nonsmokers, particularly in the early period (1 year) and among patients without percutaneous coronary intervention. However, because of the lack of original adjusted data, smoker's paradox still needs to consider the impact of age and other covariates. Thus, a differential risk-benefit evaluation should be considered, according to different smoking status, patient conditions, and therapy time points.
Keywords: effectiveness; meta‐analysis; platelet aggregation inhibitors; safety; smoking.
Figures




















Similar articles
-
Comparison of P2Y12 Inhibitors in Acute Coronary Syndromes in the Australian Population.Heart Lung Circ. 2022 Aug;31(8):1085-1092. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2022.03.007. Epub 2022 May 17. Heart Lung Circ. 2022. PMID: 35589483
-
Prasugrel or ticagrelor relative to clopidogrel in triple-antiplatelet treatment combined with glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor for patients with STEMI undergoing PCI: a meta-analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020 Mar 12;20(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01403-6. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. PMID: 32164560 Free PMC article.
-
Physician and Hospital Utilization of P2Y12 Inhibitors in ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction in the United States: A Study From the National Cardiovascular Data Registry's Research to Practice Initiative.Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020 Mar;13(3):e006275. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.119.006275. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020. PMID: 32156164
-
Safety and Effectiveness of Contemporary P2Y12 Inhibitors in an East Asian Population With Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Jul 16;8(14):e012078. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012078. Epub 2019 Jul 16. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31310570 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Antiplatelet Therapy After Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Review.JAMA. 2021 Apr 20;325(15):1545-1555. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.0716. JAMA. 2021. PMID: 33877270 Review.
Cited by
-
Subsequent ischemic stroke and tobacco smoking: A secondary analysis of the POINT trial.Eur Stroke J. 2023 Mar;8(1):328-333. doi: 10.1177/23969873221148224. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Eur Stroke J. 2023. PMID: 37021190 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ferri N, Corsini A, Bellosta S. Pharmacology of the new P2Y12 receptor inhibitors: insights on pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. Drugs. 2013;73:1681–1709. - PubMed
-
- Mehta SR, Bassand JP, Chrolavicius S, Diaz R, Fox KA, Granger CB, Jolly S, Rupprecht HJ, Widimsky P, Yusuf S; CURRENT‐OASIS 7 Steering Committee . Design and rationale of CURRENT‐OASIS 7: a randomized, 2 x 2 factorial trial evaluating optimal dosing strategies for clopidogrel and aspirin in patients with ST and non‐ST elevation acute coronary syndromes managed with an early invasive strategy. Am Heart J. 2008;156:1080–1088. - PubMed
-
- CURRENT‐OASIS 7 Investigators , Mehta SR, Bassand JP, Chrolavicius S, Diaz R, Eikelboom JW, Fox KA, Granger CB, Jolly S, Joyner CD, Rupprecht HJ, Widimsky P, Afzal R, Pogue J, Yusuf S. Dose comparisons of clopidogrel and aspirin in acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:930–942. - PubMed
-
- Mehta SR, Tanguay JF, Eikelboom JW, Jolly SS, Joyner CD, Granger CB, Faxon DP, Rupprecht HJ, Budaj A, Avezum A, Widimsky P, Steg PG, Bassand JP, Montalescot G, Macaya C, Di Pasquale G, Niemela K, Ajani AE, White HD, Chrolavicius S, Gao P, Fox KA, Yusuf S; CURRENT‐OASIS 7 trial investigators . Double‐dose versus standard‐dose clopidogrel and high‐dose versus low‐dose aspirin in individuals undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention for acute coronary syndromes (CURRENT‐OASIS 7): a randomized factorial trial. Lancet. 2010;376:1233–1243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

