Targeting promiscuous heterodimerization overcomes innate resistance to ERBB2 dimerization inhibitors in breast cancer
- PMID: 30898150
- PMCID: PMC6429830
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-019-1127-y
Targeting promiscuous heterodimerization overcomes innate resistance to ERBB2 dimerization inhibitors in breast cancer
Abstract
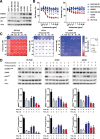
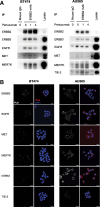
Background: The oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) ERBB2 is known to dimerize with other EGFR family members, particularly ERBB3, through which it potently activates PI3K signalling. Antibody-mediated inhibition of this ERBB2/ERBB3/PI3K axis has been a cornerstone of treatment for ERBB2-amplified breast cancer patients for two decades. However, the lack of response and the rapid onset of relapse in many patients now question the assumption that the ERBB2/ERBB3 heterodimer is the sole relevant effector target of these therapies.
Methods: Through a systematic protein-protein interaction screen, we have identified and validated alternative RTKs that interact with ERBB2. Using quantitative readouts of signalling pathway activation and cell proliferation, we have examined their influence upon the mechanism of trastuzumab- and pertuzumab-mediated inhibition of cell growth in ERBB2-amplified breast cancer cell lines and a patient-derived xenograft model.
Results: We now demonstrate that inactivation of ERBB3/PI3K by these therapeutic antibodies is insufficient to inhibit the growth of ERBB2-amplified breast cancer cells. Instead, we show extensive promiscuity between ERBB2 and an array of RTKs from outside of the EGFR family. Paradoxically, pertuzumab also acts as an artificial ligand to promote ERBB2 activation and ERK signalling, through allosteric activation by a subset of these non-canonical RTKs. However, this unexpected activation mechanism also increases the sensitivity of the receptor network to the ERBB2 kinase inhibitor lapatinib, which in combination with pertuzumab, displays a synergistic effect in single-agent resistant cell lines and PDX models.
Conclusions: The interaction of ERBB2 with a number of non-canonical RTKs activates a compensatory signalling response following treatment with pertuzumab, although a counter-intuitive combination of ERBB2 antibody therapy and a kinase inhibitor can overcome this innate therapeutic resistance.
Keywords: Breast cancer; ERBB2; Heterodimers; Pertuzumab; Receptor tyrosine kinases.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All in vivo experiments, procedures and endpoints were approved by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research Animal Ethics Committee.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Heregulin beta1 drives gefitinib-resistant growth and invasion in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9(4):R50. doi: 10.1186/bcr1754. Breast Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17686159 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired resistance to trastuzumab/pertuzumab or to T-DM1 in vivo can be overcome by HER2 kinase inhibition with TAS0728.Cancer Sci. 2020 Jun;111(6):2123-2131. doi: 10.1111/cas.14407. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 32248641 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of erbB3 with MM-121/SAR256212 enhances antitumor activity of paclitaxel against erbB2-overexpressing breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(5):R101. doi: 10.1186/bcr3563. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24168763 Free PMC article.
-
The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2014 Jan;79:34-74. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Pharmacol Res. 2014. PMID: 24269963 Review.
-
Therapeutic targeting of ERBB2 in breast cancer: understanding resistance in the laboratory and combating it in the clinic.J Mol Med (Berl). 2014 Jul;92(7):681-95. doi: 10.1007/s00109-014-1169-7. Epub 2014 May 28. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24861025 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of TRPC1 and SBEM protein in breast cancer tissue and its relationship with clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients.Oncol Lett. 2020 Dec;20(6):392. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12255. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 33193852 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted dual degradation of HER2 and EGFR obliterates oncogenic signaling, overcomes therapy resistance, and inhibits metastatic lesions in HER2-positive breast cancer models.Drug Resist Updat. 2024 May;74:101078. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2024.101078. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Drug Resist Updat. 2024. PMID: 38503142 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of pulsed cisplatin signalling dynamics identifies effectors of resistance in lung adenocarcinoma.Elife. 2020 Jun 9;9:e53367. doi: 10.7554/eLife.53367. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32513387 Free PMC article.
-
PDGFRα/β heterodimer activation negatively affects downstream ERK1/2 signaling and cellular proliferation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 27:2023.12.27.573428. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.27.573428. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 22;16(1):4754. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59938-1. PMID: 38234806 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Functional signaling test identifies HER2 negative breast cancer patients who may benefit from c-Met and pan-HER combination therapy.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Jan 8;20(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00798-9. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 34998412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cameron D, Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Gelber RD, Procter M, Goldhirsch A, de Azambuja E, Castro G, Jr, Untch M, Smith I, Gianni L, et al. 11 years’ follow-up of trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive early breast cancer: final analysis of the HERceptin Adjuvant (HERA) trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10075):1195–1205. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32616-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

