3D models in the new era of immune oncology: focus on T cells, CAF and ECM
- PMID: 30898166
- PMCID: PMC6429763
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1086-2
3D models in the new era of immune oncology: focus on T cells, CAF and ECM
Abstract
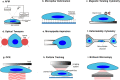
Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy has changed clinical practice for patients with different cancers, since these agents have demonstrated a significant improvement of overall survival and are effective in many patients. However, an intrinsic or acquired resistance frequently occur and biomarkers predictive of responsiveness should help in patient selection and in defining the adequate treatment options. A deep analysis of the complexity of the tumor microenvironment is likely to further advance the field and hopefully identify more effective combined immunotherapeutic strategies. Here we review the current knowledge on tumor microenvironment, focusing on T cells, cancer associated fibroblasts and extracellular matrix. The use of 3D cell culture models to resemble tumor microenvironment landscape and to screen immunomodulatory drugs is also reviewed.
Keywords: 3D culture models; Cancer associated fibroblasts; Extracellular matrix; Immune oncology; T cells; Tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Wei SC, Duffy CR, Allison JP. Fundamental mechanisms of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(9):1069–1086. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0367. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

