Vagus Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Epilepsy
- PMID: 30898273
- PMCID: PMC6432928
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nec.2018.12.005
Vagus Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Epilepsy
Abstract
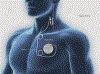
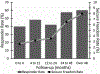
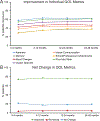
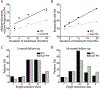
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) was the first neuromodulation device approved for treatment of epilepsy. In more than 20 years of study, VNS has consistently demonstrated efficacy in treating epilepsy. After 2 years, approximately 50% of patients experience at least 50% reduced seizure frequency. Adverse events with VNS treatment are rare and include surgical adverse events (including infection, vocal cord paresis, and so forth) and stimulation side effects (hoarseness, voice change, and cough). Future developments in VNS, including closed-loop and noninvasive stimulation, may reduce side effects or increase efficacy of VNS.
Keywords: Epilepsy; Epilepsy surgery; Neuromodulation; Seizures; Vagus nerve stimulator.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE STATEMENT
The Authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures