Clioquinol: To harm or heal
- PMID: 30898518
- PMCID: PMC6571072
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.03.009
Clioquinol: To harm or heal
Abstract
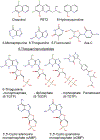
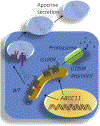
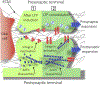
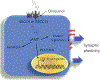
Clioquinol, one of the first mass-produced drugs, was considered safe and efficacious for many years. It was used as an antifungal and an antiprotozoal drug until it was linked to an outbreak of subacute myelo-optic neuropathy (SMON), a debilitating disease almost exclusively confined to Japan. Today, new information regarding clioquinol targets and its mechanism of action, as well as genetic variation (SNPs) in efflux transporters in the Japanese population, provide a unique interpretation of the existing phenomena. Further understanding of clioquinol's role in the inhibition of cAMP efflux and promoting apoptosis might offer promise for the treatment of cancer and/or neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we highlight recent developments in the field and discuss possible connections, hypotheses and perspectives in clioquinol-related research.
Keywords: ABC transporters; Alzheimer's disease; Cancer; Clioquinol; Neurodegenerative diseases; Pharmacogenomics; SNPs.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ayton S, Lei P, & Bush AI (2013). Metallostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med, 62, 76–89. - PubMed
-
- Ban H, Andoh A, Imaeda H, Kobori A, Bamba S, Tsujikawa T, Sasaki M, Saito Y, & Fujiyama Y (2010). The multidrug-resistance protein 4 polymorphism is a new factor accounting for thiopurine sensitivity in Japanese patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol, 45, 1014–1021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

