Cross Talk with the GAR-3 Receptor Contributes to Feeding Defects in Caenorhabditis elegans eat-2 Mutants
- PMID: 30898771
- PMCID: PMC6499512
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.119.302053
Cross Talk with the GAR-3 Receptor Contributes to Feeding Defects in Caenorhabditis elegans eat-2 Mutants
Abstract
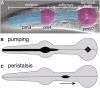
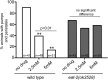
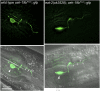
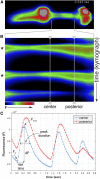
Precise signaling at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) is essential for proper muscle contraction. In the Caenorhabditis elegans pharynx, acetylcholine (ACh) released from the MC and M4 motor neurons stimulates two different types of contractions in adjacent muscle cells, termed pumping and isthmus peristalsis. MC stimulates rapid pumping through the nicotinic ACh receptor EAT-2, which is tightly localized at the MC NMJ, and eat-2 mutants exhibit a slow pump rate. Surprisingly, we found that eat-2 mutants also hyperstimulated peristaltic contractions, and that they were characterized by increased and prolonged Ca2+ transients in the isthmus muscles. This hyperstimulation depends on cross talk with the GAR-3 muscarinic ACh receptor as gar-3 mutation specifically suppressed the prolonged contraction and increased Ca2+ observed in eat-2 mutant peristalses. Similar GAR-3-dependent hyperstimulation was also observed in mutants lacking the ace-3 acetylcholinesterase, and we suggest that NMJ defects in eat-2 and ace-3 mutants result in ACh stimulation of extrasynaptic GAR-3 receptors in isthmus muscles. gar-3 mutation also suppressed slow larval growth and prolonged life span phenotypes that result from dietary restriction in eat-2 mutants, indicating that cross talk with the GAR-3 receptor has a long-term impact on feeding behavior and eat-2 mutant phenotypes.
Keywords: C. elegans; GCaMP3; feeding; life span; muscarinic acetylcholine receptor; nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; peristalsis; pharynx.
Copyright © 2019 Kozlova, et al.
Figures




Similar articles
-
G alpha(q)-coupled muscarinic acetylcholine receptors enhance nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans mating behavior.J Neurosci. 2007 Feb 7;27(6):1411-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4320-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17287516 Free PMC article.
-
eat-2 and eat-18 are required for nicotinic neurotransmission in the Caenorhabditis elegans pharynx.Genetics. 2004 Jan;166(1):161-9. doi: 10.1534/genetics.166.1.161. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15020415 Free PMC article.
-
Extrasynaptic acetylcholine signaling through a muscarinic receptor regulates cell migration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 5;118(1):e1904338118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1904338118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33361149 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans feeding.WormBook. 2012 May 21:1-23. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.150.1. WormBook. 2012. PMID: 22628186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonergic modulation of feeding behavior in Caenorhabditis elegans and other related nematodes.Neurosci Res. 2020 May;154:9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Neurosci Res. 2020. PMID: 31028772 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Profiling of a Brugia malayi Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor as a Putative Antiparasitic Target.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023 Jan 24;67(1):e0118822. doi: 10.1128/aac.01188-22. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023. PMID: 36602350 Free PMC article.
-
Novel actions of arecoline in the C. elegans motor circuit.MicroPubl Biol. 2020 Jul 1;2020:10.17912/micropub.biology.000275. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000275. MicroPubl Biol. 2020. PMID: 32666042 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
An hourglass circuit motif transforms a motor program via subcellularly localized muscle calcium signaling and contraction.Elife. 2021 Jul 2;10:e59341. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59341. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34212858 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the underlying mechanisms of the pharyngeal pumping motions in Caenorhabditis elegans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 13;121(7):e2302660121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2302660121. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38315866 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling organophosphate intoxication in C. elegans highlights nicotinic acetylcholine receptor determinants that mitigate poisoning.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 21;18(4):e0284786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284786. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37083685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel F. M., 1990. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley-Interscience, New York.
-
- Avery L., 1993b Motor neuron M3 controls pharyngeal muscle relaxation timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Exp. Biol. 175: 283–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

