Extracellular Matrix Protein Tenascin C Increases Phagocytosis Mediated by CD47 Loss of Function in Glioblastoma
- PMID: 30898840
- PMCID: PMC8218246
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3125
Extracellular Matrix Protein Tenascin C Increases Phagocytosis Mediated by CD47 Loss of Function in Glioblastoma
Abstract
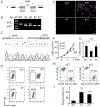
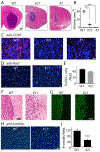
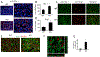
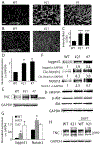
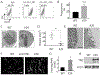
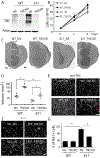
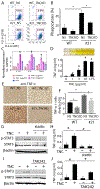
Glioblastomas (GBM) are highly infiltrated by myeloid-derived innate immune cells that contribute to the immunosuppressive nature of the brain tumor microenvironment (TME). CD47 has been shown to mediate immune evasion, as the CD47-SIRPα axis prevents phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages and other myeloid cells. In this study, we established CD47 homozygous deletion (CD47-/-) in human and mouse GBM cells and investigated the impact of eliminating the "don't eat me" signal on tumor growth and tumor-TME interactions. CD47 knockout (KO) did not significantly alter tumor cell proliferation in vitro but significantly increased phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages in cocultures. Compared with CD47 wild-type xenografts, orthotopic xenografts derived from CD47-/- tumor cells grew significantly slower with enhanced tumor cell phagocytosis and increased recruitment of M2-like tumor-associated microglia/macrophages (TAM). CD47 KO increased tumor-associated extracellular matrix protein tenascin C (TNC) in xenografts, which was further examined in vitro. CD47 loss of function upregulated TNC expression in tumor cells via a Notch pathway-mediated mechanism. Depletion of TNC in tumor cells enhanced the growth of CD47-/- xenografts in vivo and decreased the number of TAM. TNC knockdown also inhibited phagocytosis of CD47-/- tumor cells in cocultures. Furthermore, TNC stimulated release of proinflammatory factors including TNFα via a Toll-like receptor 4 and STAT3-dependent mechanism in human macrophage cells. These results reveal a vital role for TNC in immunomodulation in brain tumor biology and demonstrate the prominence of the TME extracellular matrix in affecting the antitumor function of brain innate immune cells. SIGNIFICANCE: These findings link TNC to CD47-driven phagocytosis and demonstrate that TNC affects the antitumor function of brain TAM, facilitating the development of novel innate immune system-based therapies for brain tumors.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microglia membrane-mediated trans-blood-brain barrier prodrug micelles enhance phagocytosis for glioblastoma chemo-immunotherapy.J Control Release. 2025 Feb 10;378:932-948. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.12.059. Epub 2025 Jan 1. J Control Release. 2025. PMID: 39724944
-
Microglia are effector cells of CD47-SIRPα antiphagocytic axis disruption against glioblastoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jan 15;116(3):997-1006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1721434116. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30602457 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microenvironment tenascin-C promotes glioblastoma invasion and negatively regulates tumor proliferation.Neuro Oncol. 2016 Apr;18(4):507-17. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov171. Epub 2015 Aug 27. Neuro Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26320116 Free PMC article.
-
Tenascin-C Function in Glioma: Immunomodulation and Beyond.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1272:149-172. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-48457-6_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32845507 Review.
-
The role of CD47-SIRPα immune checkpoint in tumor immune evasion and innate immunotherapy.Life Sci. 2021 May 15;273:119150. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119150. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33662426 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances on the roles of tenascin-C in cancer.J Cell Sci. 2022 Sep 15;135(18):jcs260244. doi: 10.1242/jcs.260244. Epub 2022 Sep 14. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 36102918 Free PMC article.
-
The role of tenascin-C in tumor microenvironments and its potential as a therapeutic target.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Feb 19;13:1554312. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1554312. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40046232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Glioblastoma and the Interactions with Its Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 10;15(24):5790. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245790. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the role of CD47 in cancer immunotherapy.J Adv Res. 2024 Sep;63:129-158. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.10.009. Epub 2023 Oct 28. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 39167629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutant IDH1 promotes phagocytic function of microglia/macrophages in gliomas by downregulating ICAM1.Cancer Lett. 2021 Oct 1;517:35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.05.038. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 34098063 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

