Glycogenic hepatopathy as a cause of severe deranged liver enzymes in a young patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 30898943
- PMCID: PMC6453433
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-228524
Glycogenic hepatopathy as a cause of severe deranged liver enzymes in a young patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
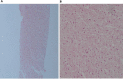
Glycogenic hepatopathy (GH) is a rare complication of poorly controlled type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). We present a 19-year-old woman with T1DM and autoimmune thyroiditis who admitted to our department because of abrupt onset intermittent abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant accompanied by laboratory evidence of acute anicteric hepatitis. Physical examination revealed significant hepatomegaly but the common imagining studies were negative. Following exclusion of common causes of acute hepatitis and because of the presence of smooth muscle antibodies in a young female patient with already established two autoimmune diseases, a liver biopsy was performed in order to exclude the potential presence of autoimmune hepatitis. However, liver histology showed typical findings of GH. Intense treatment targeting strict glycemic control resulted in normalisation of liver biochemistry. This case underlines that GH should be considered as a rare cause of acute hepatitis in T1DM patients with poor glycemic control.
Keywords: diabetes; hepatitis other; metabolic disorders; pathology.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2019. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Mauriac P. [Hepatomegaly, dwarfism, obesity and diabetes in children: Mauriac’s syndrome]. Vida Nueva 1951;67:57–65. - PubMed
-
- Torbenson M, Chen YY, Brunt E, et al. . Glycogenic hepatopathy: an underrecognized hepatic complication of diabetes mellitus. Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:508–13. - PubMed
-
- Messeri S, Messerini L, Vizzutti F, et al. . Glycogenic hepatopathy associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus as a cause of recurrent liver damage. Ann Hepatol 2012;11:554–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
