Bioinformatics analysis revealing prognostic significance of RRM2 gene in breast cancer
- PMID: 30898978
- PMCID: PMC6454020
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20182062
Bioinformatics analysis revealing prognostic significance of RRM2 gene in breast cancer
Abstract
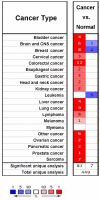
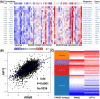
Background: Ribonucleotide reductase M2 subunit (RRM2) plays vital roles in many cellular processes such as cell proliferation, invasiveness, migration, angiogenesis, senescence, and tumorigenesis. However, the prognostic significance of RRM2 gene in breast cancer remains to be investigated. Methods:RRM2 expression was initially evaluated using the Oncomine database. The relevance between RRM2 level and clinical parameters as well as survival data in breast cancer was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier Plotter, PrognoScan, and Breast Cancer Gene-Expression Miner (bc-GenExMiner) databases. Results:RRM2 was overexpressed in different subtypes of breast cancer patients. Estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) were negatively correlated with RRM2 expression. Conversely, the Scarff-Bloom-Richardson (SBR) grade, Nottingham prognostic index (NPI), human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER-2) status, nodal status, basal-like status, and triple-negative status were positively related to RRM2 level in breast cancer samples with respect to normal tissues. Patients with increased RRM2 showed worse overall survival, relapse-free survival, distant metastasis-free survival, disease-specific survival, and disease-free survival. RRM2 also exerted positive effect on metastatic relapse event. Besides, a positive correlation between RRM2 and KIF11 genes was confirmed. Conclusion: Bioinformatics analysis revealed that RRM2 might be used as a predictive biomarker for prognosis of breast cancer. Further studies are needed to more precisely elucidate the value of RRM2 in evaluating breast cancer prognosis.
Keywords: Biomarker; Breast cancer; Prognosis; RRM2.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Li J., Pang J., Liu Y., Zhang J., Zhang C., Shen G.. et al. (2018) Suppression of RRM2 inhibits cell proliferation, causes cell cycle arrest and promotes the apoptosis of human neuroblastoma cells and in human neuroblastoma RRM2 is suppressed following chemotherapy. Oncol. Rep. 40, 355–360 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

