Liquid metal-filled magnetorheological elastomer with positive piezoconductivity
- PMID: 30899009
- PMCID: PMC6428896
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09325-4
Liquid metal-filled magnetorheological elastomer with positive piezoconductivity
Abstract
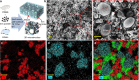
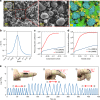
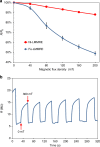
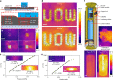
Conductive elastic composites have been used widely in soft electronics and soft robotics. These composites are typically a mixture of conductive fillers within elastomeric substrates. They can sense strain via changes in resistance resulting from separation of the fillers during elongation. Thus, most elastic composites exhibit a negative piezoconductive effect, i.e. the conductivity decreases under tensile strain. This property is undesirable for stretchable conductors since such composites may become less conductive during deformation. Here, we report a liquid metal-filled magnetorheological elastomer comprising a hybrid of fillers of liquid metal microdroplets and metallic magnetic microparticles. The composite's resistivity reaches a maximum value in the relaxed state and drops drastically under any deformation, indicating that the composite exhibits an unconventional positive piezoconductive effect. We further investigate the magnetic field-responsive thermal properties of the composite and demonstrate several proof-of-concept applications. This composite has prospective applications in sensors, stretchable conductors, and responsive thermal interfaces.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Yang T, Xie D, Li Z, Zhu H. Recent advances in wearable tactile sensors: materials, sensing mechanisms, and device performance. Mater. Sci. Eng., R. 2017;115:1–37. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2017.02.001. - DOI
-
- Lu D., Luo S. & Wong C. Conductive polymer composites. Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and TechnologyWiley10.1002/0471440264.pst430 (2004).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

