CXCR6-Deficiency Improves the Control of Pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Influenza Infection Independent of T-Lymphocyte Recruitment to the Lungs
- PMID: 30899256
- PMCID: PMC6416161
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00339
CXCR6-Deficiency Improves the Control of Pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Influenza Infection Independent of T-Lymphocyte Recruitment to the Lungs
Abstract
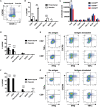
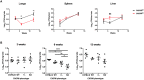
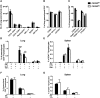
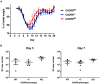
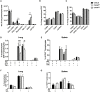
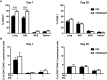
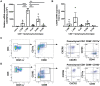
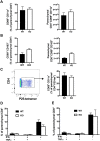
T-lymphocytes are critical for protection against respiratory infections, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and influenza virus, with chemokine receptors playing an important role in directing these cells to the lungs. CXCR6 is expressed by activated T-lymphocytes and its ligand, CXCL16, is constitutively expressed by the bronchial epithelia, suggesting a role in T-lymphocyte recruitment and retention. However, it is unknown whether CXCR6 is required in responses to pulmonary infection, particularly on CD4+ T-lymphocytes. Analysis of CXCR6-reporter mice revealed that in naïve mice, lung leukocyte expression of CXCR6 was largely restricted to a small population of T-lymphocytes, but this population was highly upregulated after either infection. Nevertheless, pulmonary infection of CXCR6-deficient mice with M. tuberculosis or recombinant influenza A virus expressing P25 peptide (rIAV-P25), an I-Ab-restricted epitope from the immunodominant mycobacterial antigen, Ag85B, demonstrated that the receptor was redundant for recruitment of T-lymphocytes to the lungs. Interestingly, CXCR6-deficiency resulted in reduced bacterial burden in the lungs 6 weeks after M. tuberculosis infection, and reduced weight loss after rIAV-P25 infection compared to wild type controls. This was paradoxically associated with a decrease in Th1-cytokine responses in the lung parenchyma. Adoptive transfer of P25-specific CXCR6-deficient T-lymphocytes into WT mice revealed that this functional change in Th1-cytokine production was not due to a T-lymphocyte intrinsic mechanism. Moreover, there was no reduction in the number or function of CD4+ and CD8+ tissue resident memory cells in the lungs of CXCR6-deficient mice. Although CXCR6 was not required for T-lymphocyte recruitment or retention in the lungs, CXCR6 influenced the kinetics of the inflammatory response so that deficiency led to increased host control of M. tuberculosis and influenza virus.
Keywords: CXCR6; influenza; lung; tissue-resident memory; tuberculosis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

