Serum Amyloid A Stimulates Vascular and Renal Dysfunction in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice Fed a Normal Chow Diet
- PMID: 30899260
- PMCID: PMC6416175
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00380
Serum Amyloid A Stimulates Vascular and Renal Dysfunction in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice Fed a Normal Chow Diet
Abstract
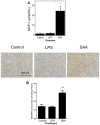
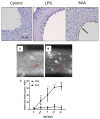
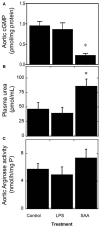
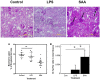
Elevated serum amyloid A (SAA) levels may promote endothelial dysfunction, which is linked to cardiovascular and renal pathologies. We investigated the effect of SAA on vascular and renal function in apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE-/-) mice. Male ApoE-/- mice received vehicle (control), low-level lipopolysaccharide (LPS), or recombinant human SAA by i.p. injection every third day for 2 weeks. Heart, aorta and kidney were harvested between 3 days and 18 weeks after treatment. SAA administration increased vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1 expression and circulating monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1 and decreased aortic cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), consistent with SAA inhibiting nitric oxide bioactivity. In addition, binding of labeled leukocytes to excised aorta increased as monitored using an ex vivo leukocyte adhesion assay. Renal injury was evident 4 weeks after commencement of SAA treatment, manifesting as increased plasma urea, urinary protein, oxidized lipids, urinary kidney injury molecule (KIM)-1 and multiple cytokines and chemokines in kidney tissue, relative to controls. Phosphorylation of nuclear-factor-kappa-beta (NFκB-p-P65), tissue factor (TF), and macrophage recruitment increased in kidneys from ApoE-/- mice 4 weeks after SAA treatment, confirming that SAA elicited a pro-inflammatory and pro-thrombotic phenotype. These data indicate that SAA impairs endothelial and renal function in ApoE-/- mice in the absence of a high-fat diet.
Keywords: acute-phase protein; endothelial function; inflammation; nitric oxide; renal dysfunction.
Figures

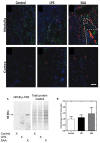
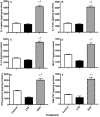
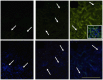
Similar articles
-
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Inhibits Serum Amyloid A (SAA)-Induced Vascular and Renal Dysfunctions in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 15;21(4):1316. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041316. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32075280 Free PMC article.
-
NFκB Inhibition Mitigates Serum Amyloid A-Induced Pro-Atherogenic Responses in Endothelial Cells and Leukocyte Adhesion and Adverse Changes to Endothelium Function in Isolated Aorta.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 28;20(1):105. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010105. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30597899 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic Nitroxide 4-Methoxy-Tempo May Decrease Serum Amyloid A-Mediated Renal Fibrosis and Reorganise Collagen Networks in Aortic Plaque.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 18;25(14):7863. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147863. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063104 Free PMC article.
-
Role of serum amyloid A in atherosclerosis.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2019 Aug;30(4):320-325. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000616. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2019. PMID: 31135596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cytokine-serum amyloid A-chemokine network.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016 Aug;30:55-69. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.12.010. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016. PMID: 26794452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current views on selenoprotein S in the pathophysiological processes of diabetes-induced atherosclerosis: potential therapeutics and underlying biomarkers.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Jan 3;16(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13098-023-01247-y. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38172976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Amyloid A3 Promoter-Driven Luciferase Activity Enables Visualization of Diabetic Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 14;23(2):899. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020899. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055081 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Amyloid A Proteins and Their Impact on Metastasis and Immune Biology in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 25;13(13):3179. doi: 10.3390/cancers13133179. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Density Lipoproteins and Serum Amyloid A (SAA).Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2021 Jan 15;23(2):7. doi: 10.1007/s11883-020-00901-4. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2021. PMID: 33447953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro-Inflammatory Serum Amyloid a Stimulates Renal Dysfunction and Enhances Atherosclerosis in Apo E-Deficient Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 22;22(22):12582. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212582. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Panza JA, Garcia CE, Kilcoyne CM, Quyyumi AA, Cannon RO., III Impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation in patients with essential hypertension. Evidence that nitric oxide abnormality is not localized to a single signal transduction pathway. Circulation. (1995) 91:1732–8. 10.1161/01.CIR.91.6.1732 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

