Drosophila mRNA Localization During Later Development: Past, Present, and Future
- PMID: 30899273
- PMCID: PMC6416162
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00135
Drosophila mRNA Localization During Later Development: Past, Present, and Future
Abstract
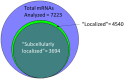
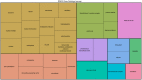
Multiple mechanisms tightly regulate mRNAs during their transcription, translation, and degradation. Of these, the physical localization of mRNAs to specific cytoplasmic regions is relatively easy to detect; however, linking localization to functional regulatory roles has been more difficult to establish. Historically, Drosophila melanogaster is a highly effective model to identify localized mRNAs and has helped identify roles for this process by regulating various cell activities. The majority of the well-characterized functional roles for localizing mRNAs to sub-regions of the cytoplasm have come from the Drosophila oocyte and early syncytial embryo. At present, relatively few functional roles have been established for mRNA localization within the relatively smaller, differentiated somatic cell lineages characteristic of later development, beginning with the cellular blastoderm, and the multiple cell lineages that make up the gastrulating embryo, larva, and adult. This review is divided into three parts-the first outlines past evidence for cytoplasmic mRNA localization affecting aspects of cellular activity post-blastoderm development in Drosophila. The majority of these known examples come from highly polarized cell lineages such as differentiating neurons. The second part considers the present state of affairs where we now know that many, if not most mRNAs are localized to discrete cytoplasmic regions in one or more somatic cell lineages of cellularized embryos, larvae or adults. Assuming that the phenomenon of cytoplasmic mRNA localization represents an underlying functional activity, and correlation with the encoded proteins suggests that mRNA localization is involved in far more than neuronal differentiation. Thus, it seems highly likely that past-identified examples represent only a small fraction of localization-based mRNA regulation in somatic cells. The last part highlights recent technological advances that now provide an opportunity for probing the role of mRNA localization in Drosophila, moving beyond cataloging the diversity of localized mRNAs to a similar understanding of how localization affects mRNA activity.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster; epithelial differentiation; mRNA localization; neuronal differentiation; organelle.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

