A systematic review and meta-analysis on the treatment of liver hydatid cyst using meta-MUMS tool: comparing PAIR and laparoscopic procedures
- PMID: 30899281
- PMCID: PMC6425195
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2018.73344
A systematic review and meta-analysis on the treatment of liver hydatid cyst using meta-MUMS tool: comparing PAIR and laparoscopic procedures
Abstract
Introduction: There is an academic debate over surgical treatments of liver hydatid cyst disease. In this study, a systematic review and meta-analysis were carried out in order to evaluate the pros and cons of both PAIR (Puncture, Aspiration, Injection, Respiration) and laparoscopic techniques by considering the outcomes of liver hydatid cysts.
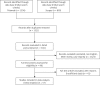
Material and methods: We designed descriptive Boolean queries to search two databases, PubMed and Scopus, to derive the articles published in the period of January 2000 to December 2016 in order to evaluate the outcomes of these research articles. The outcomes of laparoscopic and PAIR procedures include the rates of cure, postoperative complications, recurrences, and mortality, which were extracted, assessed, and used as their corresponding effect sizes.
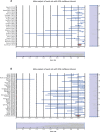
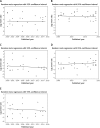
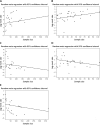
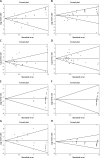
Results: Fifty-seven studies including a total of 2832 patients (PAIR group n = 1650 and laparoscopic group = 1182) were analyzed. In this meta-analysis study, a random effect model of correlations of outcomes (postoperative complications, mortalities, recurrences, and cure rates) of PAIR and laparoscopy procedures was used. The meta-analysis and the forest plots of the two procedures show that the PAIR approach is superior in terms of cure, complication, and mortality rates compared with the laparoscopy technique. However, the recurrence rate is low in laparoscopic approaches. Moreover, Egger's tests for determining publication bias and heterogeneity tests were also performed.
Conclusions: This study shows promising trends toward an advantage of PAIR procedures in treatment of liver hydatid cyst in comparison with laparoscopic procedures. The PAIR procedure is superior to laparoscopy due to having a higher cure rate and lower complication and mortality rates; however, the latter has a lower recurrence rate.
Keywords: PAIR; echinococcosis; hydatid cyst; laparoscopy; liver; meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Comparison of 2 New Promising Weapons for the Treatment of Hydatid Cyst Disease: PAIR and Laparoscopic Therapy.Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2015 Aug;25(4):358-62. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000177. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2015. PMID: 26241297 Review.
-
Therapeutic Options in Hydatid Hepatic Cyst Surgery: A Retrospective Analysis of Three Surgical Approaches.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 30;14(13):1399. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14131399. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001289 Free PMC article.
-
Current approaches in the surgical treatment of liver hydatid disease: single center experience.BMC Surg. 2019 Jul 17;19(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12893-019-0553-1. BMC Surg. 2019. PMID: 31315619 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the treatment of liver hydatid cysts.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 7;21(1):124-31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.124. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25574085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Results of surgical, laparoscopic, and percutaneous treatment for hydatid disease of the liver: 10 years experience with 355 patients.World J Surg. 2005 Dec;29(12):1670-9. doi: 10.1007/s00268-005-0058-1. World J Surg. 2005. PMID: 16311852
Cited by
-
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell (BM-MSC): A tool of cell therapy in hydatid experimentally infected rats.Cell Regen. 2019 Nov 21;8(2):58-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cr.2019.11.001. eCollection 2019 Dec. Cell Regen. 2019. PMID: 31844519 Free PMC article.
-
Complicated Liver Cystic Echinococcosis-A Comprehensive Literature Review and a Tale of Two Extreme Cases.Tomography. 2024 Jun 11;10(6):922-934. doi: 10.3390/tomography10060070. Tomography. 2024. PMID: 38921947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute liver failure secondary to toxic exposure in children.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Sep 9;18(1):84-91. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.87716. eCollection 2022. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 35154529 Free PMC article.
-
Serum vitamin D deficiency and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis.Arch Med Sci. 2020 Apr 15;16(4):742-751. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2020.94433. eCollection 2020. Arch Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32542074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silybum marianum ethanolic extract: in vitro effects on protoscolices of Echinococcus granulosus G1 strain with emphasis on other Iranian medicinal plants.Trop Med Health. 2021 Sep 8;49(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s41182-021-00363-7. Trop Med Health. 2021. PMID: 34496975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen X, Cen C, Xie H, et al. The comparison of 2 new promising weapons for the treatment of hydatid cyst disease: PAIR and laparoscopic therapy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2015;25:358–62. - PubMed
-
- Symeonidis N, Pavlidis T, Baltatzis M, et al. Complicated liver echinococcosis: 30 years of experience from an endemic area. Scand J Surg. 2013;102:171–7. - PubMed
-
- Yagci G, Ustunsoz B, Kaymakcioglu N, et al. Results of surgical, laparoscopic, and percutaneous treatment for hydatid disease of the liver: 10 years experience with 355 patients. World J Surg. 2005;29:1670–9. - PubMed
-
- Polat FR. Hydatid cyst: open or laparoscopic approach? A retrospective analysis. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2012;22:264–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
