Expression of tryptophan hydroxylase in gastric mucosa in symptomatic and asymptomatic Helicobacter pylori infection
- PMID: 30899295
- PMCID: PMC6425205
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2018.76928
Expression of tryptophan hydroxylase in gastric mucosa in symptomatic and asymptomatic Helicobacter pylori infection
Abstract
Introduction: Helicobacter pylori infection induces clinical symptoms in 15-20% of subjects, and the reason for this variation is still not clear. The aim of the present study is to evaluate the expression of tryptophan hydroxylase (TpH-1) in gastric mucosa of patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic H. pylori infection in relation to the intensity of bacterial colonization and severity of dyspeptic symptoms.
Material and methods: Ninety subjects (aged 35-49 years) were enrolled in the study and separated into 3 groups of 30 subjects each. Group I - healthy volunteers without H. pylori infection, group II - subjects with asymptomatic H. pylori infection, group III - H. pylori-infected patients with dyspeptic symptoms, mainly fasting and nocturnal epigastric pain. To diagnose H. pylori infection the urea breath test (UBT-13C) and histological analysis were performed. The level of mRNA expression of tryptophan hydroxylase (TpH-1) was estimated in gastric mucosa with RT-PCR.
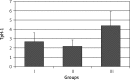
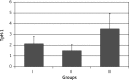
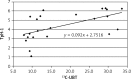
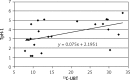
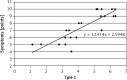
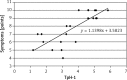
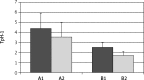
Results: The expression of this enzyme in antral mucosa was 2.69 ±0.97 in group I, 2.28 ±0.69 in group II (p > 0.05) and 4.40 ±1.64 in group III (p < 0.001). The levels of expression of TpH-1 in gastric body mucosa were 2.16 ±0.70, 1.57 ±0.52 (p > 0.05) and 3.40 ±1.51 (p < 0.001), respectively. In group III a positive correlation was found between intensity of H. pylori colonization and TpH-1 expression as well as between TpH-1 expression and severity of dyspeptic symptoms.
Conclusions: Increased expression of TpH-1 in gastric mucosa plays a role in pathogenesis of chronic dyspepsia.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; chronic dyspepsia; gastric mucosa; tryptophan hydroxylase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The clinical significance of GastroPanel in diagnostics of Helicobacter pylori eradication efficiency in patients with dyspepsia with correlation of family history of gastric cancer].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2013 Sep;35(207):141-7. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2013. PMID: 24224450 Polish.
-
Density of gastric Helicobacter pylori colonization is not associated with occurrence of dyspeptic symptoms.Dig Dis Sci. 1997 Oct;42(10):2120-3. doi: 10.1023/a:1018886905516. Dig Dis Sci. 1997. PMID: 9365146
-
In dyspeptic patients without gastric phase III of the migrating motor complex, Helicobacter pylori eradication produces no short-term changes in interdigestive motility pattern.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000 Aug;35(8):808-13. doi: 10.1080/003655200750023165. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000. PMID: 10994618 Clinical Trial.
-
[The assessment of nitric oxide metabolites in gastric juice in Helicobacter pylori infected subjects in compliance with grade of inflammatory lesions in gastric mucosa].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008 Feb;24(140):95-100. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008. PMID: 18634262 Polish.
-
Accuracy of urea breath test in Helicobacter pylori infection: meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 28;21(4):1305-14. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i4.1305. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25632206 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Tumor Microenvironment in Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric Cancer.Cells. 2020 Apr 23;9(4):1055. doi: 10.3390/cells9041055. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32340207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extraction of antibacterial peptides against Helicobacter pylori from bovine milk casein.Arch Med Sci. 2021 Mar 24;18(2):376-381. doi: 10.5114/aoms/109942. eCollection 2022. Arch Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 35316909 Free PMC article.
-
FTO-mediated m6A modification promotes malignant transformation of gastric mucosal epithelial cells in chronic Cag A+ Helicobacter pylori infection.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Aug;149(10):7327-7340. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04684-4. Epub 2023 Mar 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36918410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jais M, Barua S. Seroprevalence of anti Helicobacter pylori IgG/IgA in asymptomatic population from Delhi. J Commun Dis. 2004;36:132–5. - PubMed
-
- Dinić M, Tasić G, Stanković-Dordević D, Otasević L, Tasić M, Karanikolic A. Serum anti-Helicobacter pylori IgA and IgG antibodies in asymptomatic children in Serbia. Scand J Infect Dis. 2007;39:303–7. - PubMed
-
- Sumona AA, Hossain MA, Musa AK, et al. Anti H. pylori IgM in symptomatic and asymptomatic population. Mymensingh Med J. 2009;18:18–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
