Expression of tryptophan hydroxylase in gastric mucosa in symptomatic and asymptomatic Helicobacter pylori infection
- PMID: 30899295
- PMCID: PMC6425205
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2018.76928
Expression of tryptophan hydroxylase in gastric mucosa in symptomatic and asymptomatic Helicobacter pylori infection
Abstract
Introduction: Helicobacter pylori infection induces clinical symptoms in 15-20% of subjects, and the reason for this variation is still not clear. The aim of the present study is to evaluate the expression of tryptophan hydroxylase (TpH-1) in gastric mucosa of patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic H. pylori infection in relation to the intensity of bacterial colonization and severity of dyspeptic symptoms.
Material and methods: Ninety subjects (aged 35-49 years) were enrolled in the study and separated into 3 groups of 30 subjects each. Group I - healthy volunteers without H. pylori infection, group II - subjects with asymptomatic H. pylori infection, group III - H. pylori-infected patients with dyspeptic symptoms, mainly fasting and nocturnal epigastric pain. To diagnose H. pylori infection the urea breath test (UBT-13C) and histological analysis were performed. The level of mRNA expression of tryptophan hydroxylase (TpH-1) was estimated in gastric mucosa with RT-PCR.
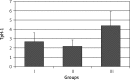
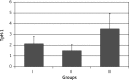
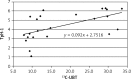
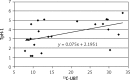
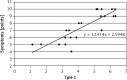
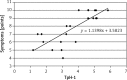
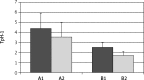
Results: The expression of this enzyme in antral mucosa was 2.69 ±0.97 in group I, 2.28 ±0.69 in group II (p > 0.05) and 4.40 ±1.64 in group III (p < 0.001). The levels of expression of TpH-1 in gastric body mucosa were 2.16 ±0.70, 1.57 ±0.52 (p > 0.05) and 3.40 ±1.51 (p < 0.001), respectively. In group III a positive correlation was found between intensity of H. pylori colonization and TpH-1 expression as well as between TpH-1 expression and severity of dyspeptic symptoms.
Conclusions: Increased expression of TpH-1 in gastric mucosa plays a role in pathogenesis of chronic dyspepsia.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; chronic dyspepsia; gastric mucosa; tryptophan hydroxylase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jais M, Barua S. Seroprevalence of anti Helicobacter pylori IgG/IgA in asymptomatic population from Delhi. J Commun Dis. 2004;36:132–5. - PubMed
-
- Dinić M, Tasić G, Stanković-Dordević D, Otasević L, Tasić M, Karanikolic A. Serum anti-Helicobacter pylori IgA and IgG antibodies in asymptomatic children in Serbia. Scand J Infect Dis. 2007;39:303–7. - PubMed
-
- Sumona AA, Hossain MA, Musa AK, et al. Anti H. pylori IgM in symptomatic and asymptomatic population. Mymensingh Med J. 2009;18:18–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
