Neuroprotective effects of the new Na channel blocker rs100642 in global ischemic brain injury
- PMID: 30899300
- PMCID: PMC6425206
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2017.72550
Neuroprotective effects of the new Na channel blocker rs100642 in global ischemic brain injury
Abstract
Introduction: RS100642, a mexiletine analogue, is a novel sodium channel blocker with neuroprotective and antioxidant activities. The protectivity of RS100642, which has been shown against focal cerebral ischemia, was investigated in global cerebral ischemia in this study.
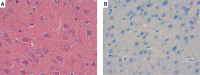
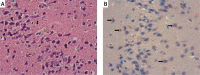
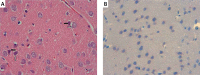
Material and methods: Global cerebral ischemia was induced for five minutes in adult male Wistar Albino rats via the 4-vessel occlusion method. Intravenous administration of 1 mg/kg RS100642 following reperfusion for 30 min (RS100642 group) was compared with a sham treatment group (ischemia group) and nonischemized group (control) histologically based on morphology and caspase-3 immunohistochemistry, and biochemically based both on measurement of oxidative stress including malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and catalase (CAT) activities and on assessment of apoptosis including caspase-3 and -8 activities and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) levels at the end of 6 h.
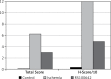
Results: While the RS100642 group had significantly lower MDA levels and higher SOD activities than the sham treatment group (p < 0.05), GPx and CAT activities of the RS100642 and sham treatment groups were similar (p > 0.05) and significantly lower than those of the controls (p < 0.05). Necrosis and caspase-3 activity and immunoreactivity in the RS100642 group were significantly lower than those in the sham treatment group (p < 0.05), while there was no significant difference between groups regarding caspase-8 and TNF-α (p > 0.05).
Conclusions: Na+ channel blockade by RS100642 has remarkable neuroprotective effects following global brain ischemia/reperfusion damage. Further research is required to determine the optimum dose and time of administration.
Keywords: brain injury; global cerebral ischemia; neuroprotection; sodium channels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The sodium channel blocker RS100642 reverses down-regulation of the sodium channel alpha-subunit Na(v) 1.1 expression caused by transient ischemic brain injury in rats.Neurotox Res. 2003;5(4):245-53. doi: 10.1007/BF03033382. Neurotox Res. 2003. PMID: 12835116
-
Neuroprotective effects of the sodium channel blocker RS100642 and attenuation of ischemia-induced brain seizures in the rat.Brain Res. 2002 Apr 5;932(1-2):45-55. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)02275-8. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 11911860
-
Pomegranate extract protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury and preserves brain DNA integrity in rats.Life Sci. 2014 Aug 21;110(2):61-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.06.023. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 25010842
-
Neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuation of inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis.J Neurosurg Spine. 2016 Jun;24(6):949-59. doi: 10.3171/2015.10.SPINE15612. Epub 2016 Feb 12. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016. PMID: 26871652
-
Anemonin alleviates nerve injury after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion (i/r) in rats by improving antioxidant activities and inhibiting apoptosis pathway.J Mol Neurosci. 2014 Jun;53(2):271-9. doi: 10.1007/s12031-013-0217-z. Epub 2014 Jan 21. J Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24443273
References
-
- Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M. Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Cell Dev Biol. 1999;15:269–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
