Development of an innovative and sustainable one-step method for rapid plant DNA isolation for targeted PCR using magnetic ionic liquids
- PMID: 30899320
- PMCID: PMC6408755
- DOI: 10.1186/s13007-019-0408-x
Development of an innovative and sustainable one-step method for rapid plant DNA isolation for targeted PCR using magnetic ionic liquids
Abstract
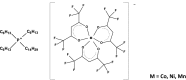
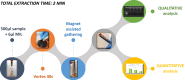
Background: Nowadays, there is an increasing demand for fast and reliable plant biomolecular analyses. Conventional methods for the isolation of nucleic acids are time-consuming and require multiple and often non-automatable steps to remove cellular interferences, with consequence that sample preparation is the major bottleneck in the bioanalytical workflow. New opportunities have been created by the use of magnetic ionic liquids (MILs) thanks to their affinity for nucleic acids.
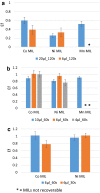
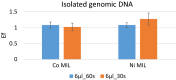
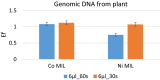
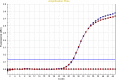
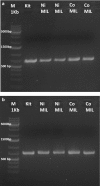
Results: In the present study, a MIL-based magnet-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (maDLLME) method was optimized for the extraction of genomic DNA from Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh leaves. MILs containing different metal centers were tested and the extraction method was optimized in terms of MIL volume and extraction time for purified DNA and crude lysates. The proposed approach yielded good extraction efficiency and is compatible with both quantitative analysis through fluorimetric-based detection and qualitative analysis as PCR amplification of multi and single locus genes. The protocol was successfully applied to a set of plant species and tissues.
Conclusions: The developed MIL-based maDLLME approach exhibits good enrichment of nucleic acids for extraction of template suitable for targeted PCR; it is very fast, sustainable and potentially automatable thereby representing a powerful tool for screening plants rapidly using DNA-based methods.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh.; DNA barcoding; DNA isolation; Magnetic ionic liquids.
Figures
References
-
- Galimberti A, De Mattia F, Losa A, Bruni I, Federici S, Casiraghi M, et al. DNA barcoding as a new tool for food traceability. Food Res Int. 2013;50(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.09.036. - DOI
-
- Marengo A, Piras A, Falconieri D, Porcedda S, Caboni P, Cortis P, et al. Chemical and biomolecular analyses to discriminate three taxa of Pistacia genus from Sardinia Island (Italy) and their antifungal activity. Nat Prod Res. 2018;32(23):2766–2774. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

