The IRE1α-XBP1 pathway function in hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling, is upregulated by quercetin, inhibits apoptosis and partially reverses the effect of quercetin in PASMCs
- PMID: 30899368
- PMCID: PMC6413268
The IRE1α-XBP1 pathway function in hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling, is upregulated by quercetin, inhibits apoptosis and partially reverses the effect of quercetin in PASMCs
Abstract
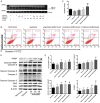
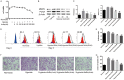
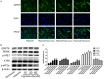
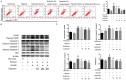
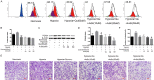
Hypoxia is a common cause of pulmonary vascular remodeling and endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS). Upon ER stress, the unfolded protein response (UPR) which activates the IRE1α, PERK and ATF6 signaling pathways is activated to cope with ERS in mammalian cells; however, the role of the three UPR arms in pulmonary vascular remodeling has not been defined. The present study showed that GRP78, a marker of ERS, was upregulated in hypoxic pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs). Among the three arms of the UPR, the IRE1α pathway was noticeably upregulated in hypoxic PASMCs. An inhibitor of IRE1α/XBP1 pathway, 4u8c, inhibited hypoxia-induced cell proliferation and migration and increased cell apoptosis by downregulating PCNA and MMP9 and activating mitochondrial apoptosis by enhancing the expression of BAX, activating caspase-9 and caspase-3, and eventually cleaving PARP. Quercetin affects ERS in many cell types and was shown to relieve hypoxic pulmonary hypertension (HPH) in our previous study. We demonstrated that quercetin evoked excessive GRP78 expression in hypoxic PASMCs compared with hypoxia alone by evaluating the expression of GRP78. The expression of IRE1α and XBP1s, a cleavage form of XBP1u, was upregulated by quercetin in a dose-dependent manner. Pretreatment with 4u8c reversed the apoptosis-promoting effect of quercetin by inhibiting mitochondrial apoptosis. However, 4u8c amplified the effect of quercetin on proliferation and migration in hypoxic PASMCs. In conclusion, the study demonstrated that the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway is involved in the process of hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling; 4u8c could restrain hypoxia-induced cell proliferation and migration and reverse the hypoxia-induced apoptosis arrest, while quercetin excited excessive ERS and the IRE1α pathway in hypoxic PASMCs and promoted apoptosis. Our data suggest that intervening the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway may be useful for hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension therapy.
Keywords: ERS; Hypoxia; IRE1α; quercetin; unfolded protein response.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Humbert M, Morrell NW, Archer SL, Stenmark KR, MacLean MR, Lang IM, Christman BW, Weir EK, Eickelberg O, Voelkel NF, Rabinovitch M. Cellular and molecular pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:13S–24S. - PubMed
-
- Dromparis P, Paulin R, Stenson TH, Haromy A, Sutendra G, Michelakis ED. Attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress as a novel therapeutic strategy in pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2013;127:115–125. - PubMed
-
- Koyama M, Furuhashi M, Ishimura S, Mita T, Fuseya T, Okazaki Y, Yoshida H, Tsuchihashi K, Miura T. Reduction of endoplasmic reticulum stress by 4-phenylbutyric acid prevents the development of hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014;306:H1314–1323. - PubMed
-
- He YY, Liu CL, Li X, Li RJ, Wang LL, He KL. Salubrinal attenuates right ventricular hypertrophy and dysfunction in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension of rats. Vascul Pharmacol. 2016;87:190–198. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
