The efficacy of physical therapy on the improvement of the motor components of visual attention in children with cerebral palsy: a case series study
- PMID: 30899744
- PMCID: PMC6416505
- DOI: 10.12965/jer.1836568.284
The efficacy of physical therapy on the improvement of the motor components of visual attention in children with cerebral palsy: a case series study
Abstract
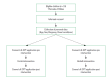
This paper has attempted to compare the effects of Bobath's concept with control's session on the improvement of visual attention in children with cerebral palsy. A 10 children sample (7 girls and 3 boys) aged 6 to 16 years (median, 12 years) was collected. The group who had received Bobath-based treatment crossed-over to control treatment and the previous control group received Bobath-based treatment for once a week. Measures were assessed at pre- and posttreatment. Outcome measure included the visual attention, we used Conners' Kiddie Continuous Performance Test (K-CPT). Bobath's session targeted to crossed-over participants produced greater improvements in K-CPT(RT) (difference=33.1, P<0.05) at posttreatment compared to the control's session group, whereas the improvement of K-CPT did not differ between groups. The results of this case series study showed a significant improvement on visual attention through the improvement of motor control functions after the Bobath's session over the control's session.
Keywords: Bobath’s concept; Cerebral Palsy; Neurodevelopmental treatment; Visual attention.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does the Conners' Continuous Performance Test aid in ADHD diagnosis?J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2000 Oct;28(5):415-24. doi: 10.1023/a:1005127504982. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2000. PMID: 11100916
-
Association of the Conners' Kiddie Continuous Performance Test (K-CPT) Performance and Parent-Report Measures of Behavior and Executive Functioning.J Atten Disord. 2018 Sep;22(11):1056-1065. doi: 10.1177/1087054715578271. Epub 2015 Apr 6. J Atten Disord. 2018. PMID: 25846228
-
Effects of Johnstone pressure splints combined with neurodevelopmental therapy on spasticity and cutaneous sensory inputs in spastic cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2001 May;43(5):307-13. doi: 10.1017/s0012162201000585. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11368483 Clinical Trial.
-
Speech rehabilitation in 10 Spanish-speaking children with severe cerebral palsy: a 4-year longitudinal study.Pediatr Rehabil. 2005 Apr-Jun;8(2):113-6. doi: 10.1080/13638490400025322. Pediatr Rehabil. 2005. PMID: 16089251
-
Neurodevelopmental Treatment (Bobath) for Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review.J Child Neurol. 2019 Oct;34(11):679-686. doi: 10.1177/0883073819852237. Epub 2019 Jun 10. J Child Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31179823
Cited by
-
Studying the Research-Practice Gap in Physical Therapies for Cerebral Palsy: Preliminary Outcomes Based on a Survey of Spanish Clinicians.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 5;19(21):14535. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192114535. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36361414 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Hippotherapy and Horse-Riding Simulators on Gross Motor Function in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 6;14(1):283. doi: 10.3390/jcm14010283. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39797365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurodevelopmental Treatment in Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Review of the Literature.Cureus. 2023 Dec 12;15(12):e50389. doi: 10.7759/cureus.50389. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38213384 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bax M, Goldstein M, Rosenbaum P, Leviton A, Paneth N, Dan B, Jacobsson B, Damiano D, Executive Committee for the Definition of Cerebral Palsy Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy, April 2005. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005;47:571–576. - PubMed
-
- He J, Dong XL, Duan YH, Zhou HL, Huang CQ, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Chen MJ. Randomized controlled study on AMIE methods for treatment of movement disorder in the child of convulsive cerebral palsy. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2007;27:797–800. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources