Molecular iodine exerts antineoplastic effects by diminishing proliferation and invasive potential and activating the immune response in mammary cancer xenografts
- PMID: 30902074
- PMCID: PMC6431076
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5437-3
Molecular iodine exerts antineoplastic effects by diminishing proliferation and invasive potential and activating the immune response in mammary cancer xenografts
Abstract
Background: The immune system is a crucial component in cancer progression or regression. Molecular iodine (I2) exerts significant antineoplastic effects, acting as a differentiation inductor and immune modulator, but its effects in antitumor immune response are not elucidated.
Methods: The present work analyzed the effect of I2 in human breast cancer cell lines with low (MCF-7) and high (MDA-MB231) metastatic potential under both in vitro (cell proliferation and invasion assay) and in vivo (xenografts of athymic nude mice) conditions.
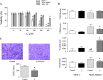
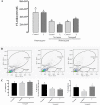
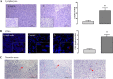
Results: In vitro analysis showed that the 200 μM I2 supplement decreases the proliferation rate in both cell lines and diminishes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) profile and the invasive capacity in MDA-MB231. In immunosuppressed mice, the I2 supplement impairs implantation (incidence), tumoral growth, and proliferation of both types of cells. Xenografts of the animals treated with I2 decrease the expression of invasion markers like CD44, vimentin, urokinase plasminogen activator and its receptor, and vascular endothelial growth factor; and increase peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Moreover, in mice with xenografts, the I2 supplement increases the circulating level of leukocytes and the number of intratumoral infiltrating lymphocytes, some of them activated as CD8+, suggesting the activation of antitumor immune responses.
Conclusions: I2 decreases the invasive potential of a triple negative basal cancer cell line, and under in vivo conditions the oral supplement of this halogen activates the antitumor immune response, preventing progression of xenografts from laminal and basal mammary cancer cells. These effects allow us to propose iodine supplementation as a possible adjuvant in breast cancer therapy.
Keywords: Immune response; Iodine; MCF-12F; MCF-7; MDA-MB231; Mammary cancer; Molecular iodine; PPARγ; Xenografts.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All procedures followed the
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

