The NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 fails to impair long-term recognition memory in mice when the state-dependency of memory is controlled
- PMID: 30902736
- PMCID: PMC6542379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2019.03.006
The NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 fails to impair long-term recognition memory in mice when the state-dependency of memory is controlled
Abstract
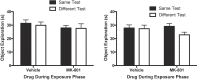
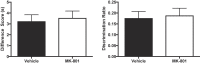
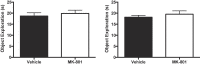
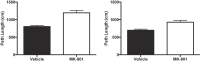
NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity has been proposed to be important for encoding of memories. Consistent with this hypothesis, the non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, MK-801, has been found to impair performance on tests of memory. Interpretation of some of these findings has, however, been complicated by the fact that the drug-state of animals has differed during encoding and tests of memory. Therefore, it is possible that MK-801 may result in state-dependent retrieval or expression of memory rather than actually impairing encoding itself. We tested this hypothesis in mice using tests of object recognition memory with a 24-hour delay between the encoding and test phase. Mice received injections of either vehicle or MK-801 prior to the encoding phase and the test phase. In Experiment 1, a low dose of MK-801 (0.01 mg/kg) impaired performance when the drug-state (vehicle or MK-801) of mice changed between encoding and test, but there was no significant effect of MK-801 on encoding. In Experiment 2, a higher dose of MK-801 (0.1 mg/kg) failed to impair object recognition memory when mice received the drug prior to both encoding and test compared to mice that received vehicle. MK-801 did not affect object exploration, but it did induce locomotor hyperactivity at the higher dose. These results suggest that some previous demonstrations of MK-801 effects may reflect a failure to express or retrieve memory due to the state-dependency of memory rather than impaired encoding of memory.
Keywords: Habituation; MK-801; Memory; Mice; NMDA receptors.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ameen-Ali K.E., Eacott M.J., Easton A. A new behavioural apparatus to reduce animal numbers in multiple types of spontaneous object recognition paradigms in rats. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 2012;211:66–76. - PubMed
-
- Ameen-Ali K.E., Easton A., Eacott M.J. Moving beyond standard procedures to assess spontaneous recognition memory. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 2015;53:37–51. - PubMed
-
- Andine P., Widermark N., Axelsson R., Nyberg G., Olofsson U., Martensson E., Sandberg M. Characterization of MK-801-induced behavior as a putative rat model of psychosis. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1999;290:1393–1408. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman D.M., Sprengel R., Sanderson D.J., McHugh S.B., Rawlins J.N., Monyer H., Seeburg P.H. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, spatial memory and anxiety. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2014;15:181–192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

